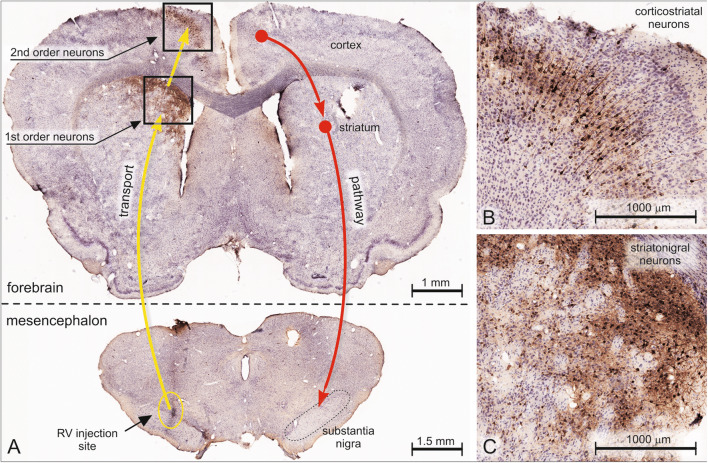
Fig. 9.
Transsynaptic retrograde tracing in rat with rabies virus (RV). a The investigated two-neuron chain schematically indicated on the right (red arrows): cerebral cortex to striatum, striatum-to-substantia nigra. The yellow arrows on the left indicate the retrograde tracing route. RV was pressure-injected into the substantia nigra. One week later, both first-order neurons (medium-sized striatal spiny striatonigral-projecting neurons) and second-order neurons (corticostriatal-projecting pyramidal neurons) could be observed. b, c Enlarged portions (the boxed areas in a). Retrograde transsynaptic spread of RV enables the accurate detection of neurons linking successively cerebral cortex, striatum, and substantia nigra. Detection of RV was with a primary antibody against a soluble rabies viral phosphoprotein, followed by a biotinylated IgG, then incubated with an HRP-tagged streptavidin and finally visualized with DAB