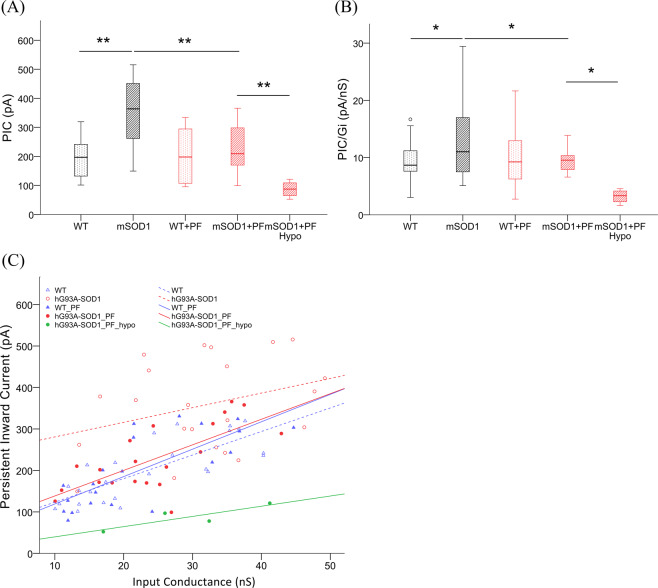
Figure 6.
PF-4708671 treatment prevents PIC enhancement in hG93A-SOD1 motoneurons. (A) PICs were significantly larger in hG93A-SOD1 motoneurons compared to WT, but not in those cells that received PF-4708671. Four out of twenty-four (17%) hG93A-SOD1 motoneurons that received PF-4708671 showed profound hypoexcitability and much smaller PICs than other motoneurons, but no significant change in input conductance (Gin). (B) The ratio of PIC to Gin was taken as a metric of altered excitability. The result showed similar trend and significant changes as in PIC analysis in (A). (C) To further investigate the relationship between PIC and input conductance, we plotted their distributions and fitted the data with a linear equation. Within a comparable input conductance range, the hG93A-SOD1 motoneurons had larger PICs. In contrast, the hG93A-SOD1 motoneurons in animals treated with PF-4708671, had smaller PICs regardless of Gin. Wild-type, WT; 30 mg/kgBW PF-4708671, PF; hypoexcitable, Hypo; persistent inward current, PIC; input conductance, Gin; **P < 0.01.