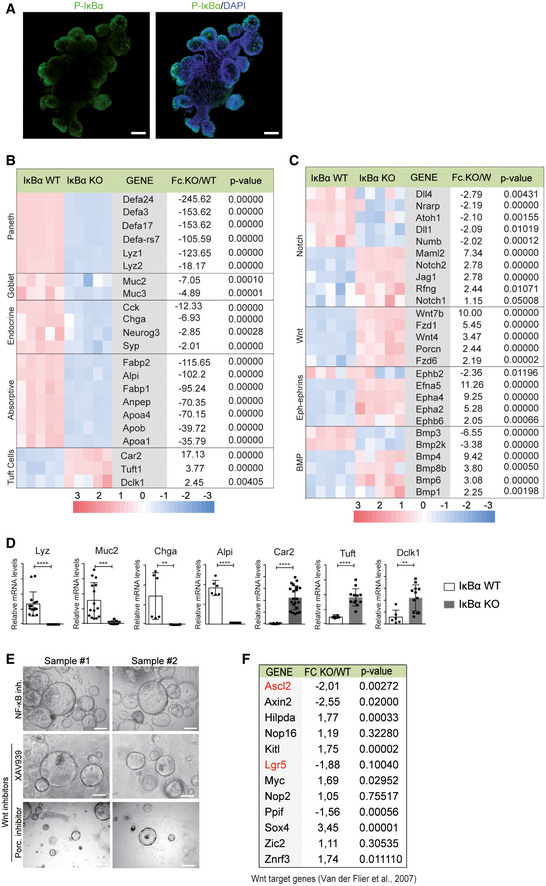
Figure EV4. P‐IκBα is expressed in organoid pockets, and its deficiency leads to transcriptional alterations in differentiation markers and pathways, which are NF‐κB‐ and Wnt/β‐catenin‐independent.
-
AIF analysis of P‐IκBα in WT organoids.
-
B, CSelection of differentially expressed genes associated with intestinal lineages (B) and molecular pathways (C) identified by microarray assay from WT and IκBα KO‐derived organoids. Five different organoids per genotype were analyzed, which were generated from at least 2 different mice per genotype.
-
DValidation of relevant genes by qPCR. Three technical replicates of a minimum of two organoids per condition were analyzed. Bars represent mean values ± standard error of the mean (s.e.m.); P values were derived from an unpaired t‐test, two‐tailed, ****P‐value < 0.0001, ***P‐value < 0.0005, **P‐value < 0.005.
-
ERepresentative stereoscopic images of IκBα KO organoids treated as indicated.
-
FTable indicating the Wnt/β‐catenin target genes 44 differentially expressed between IκBα WT and KO organoids (expression microarray, n = 5 WT and n = 5 KO). In red, Wnt target ISC genes.
