Figure 1. The primary root growth of kup9 mutants is inhibited under low‐K+ conditions.
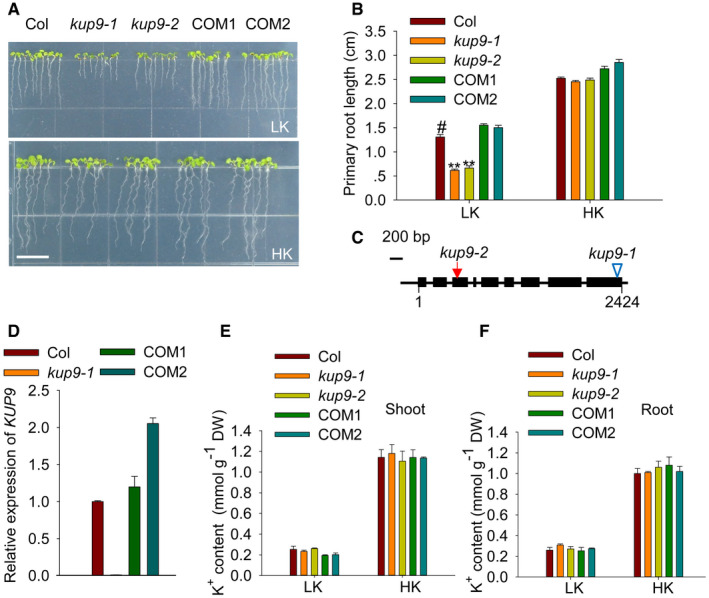
-
APhenotypes of wild type (Col), kup9 mutants (kup9‐1 and kup9‐2), and the kup9‐1/ProKUP9:KUP9 complementation lines (COM1 and COM2). Seeds were germinated and grown on low‐K+ (LK, 50 μM) or high‐K+ (HK, 5 mM) medium for 7 days. Scale bar, 1 cm.
-
BPrimary root length of the plants tested in (A). Data are means ± SE (n = 25, individual plants). Student's t‐test (**P < 0.01) was used to analyze statistical significance, and “#” represents the control.
-
CDiagram of KUP9 gene structure. The T‐DNA insertion site in the kup9‐1 mutant and the mutant site in the kup9‐2 mutant are indicated by the triangle and arrow, respectively. The filled boxes and lines represent exons and introns, respectively.
-
DRT–qPCR analysis of KUP9 transcript levels in various materials. Data are means ± SE (n = 3, biological replicates; each replicate contains 120 individual plants).
-
E, FK+ content of the various plant materials tested in (A). Data are means ± SE (n = 3, biological replicates; each replicate contains 120–150 individual plants).
Source data are available online for this figure.
