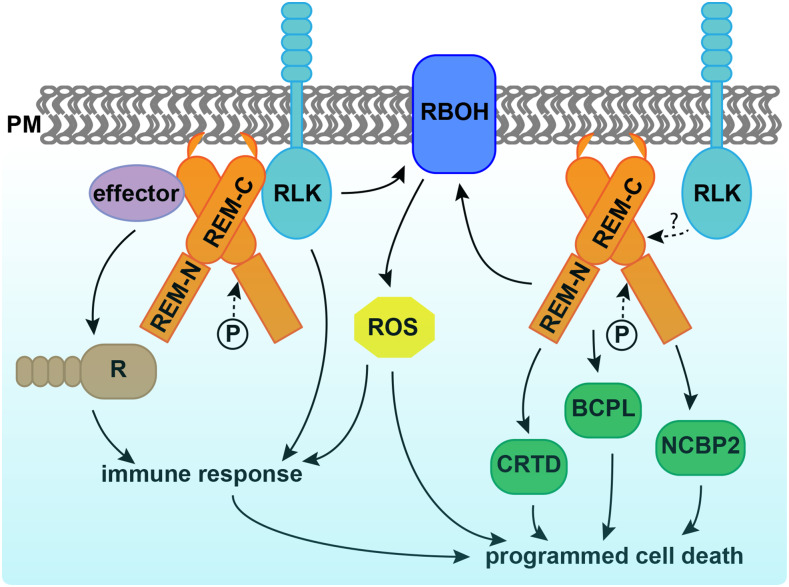
Figure 1.
REMs participate in plant-microbe interaction and PCD. REMs polymerize and physically interact with receptor-like kinases (RLK) and pathogen effectors; the latter activate R proteins and trigger immunity. The C terminus of REM (REM-C) is required for plasma membrane (PM) localization and protein interaction, while phosphorylation occurs at the N terminus (REM-N). REMs induce reaction oxygen species (ROS) and up-regulate protein abundance of CYSTEINE-RICH AND TRANSMEMBRANE DOMAIN-CONTAINING PROTEIN A-LIKE (CRTD), BLUE COPPER PROTEIN-LIKE (BCPL), NUCLEAR CAP-BINDING PROTEIN SUBUNIT 2 (NCBP2), and RBOHB in tobacco, which all contribute to programmed cell death. Whether REM induction of cell death is triggered by RLKs is not known.