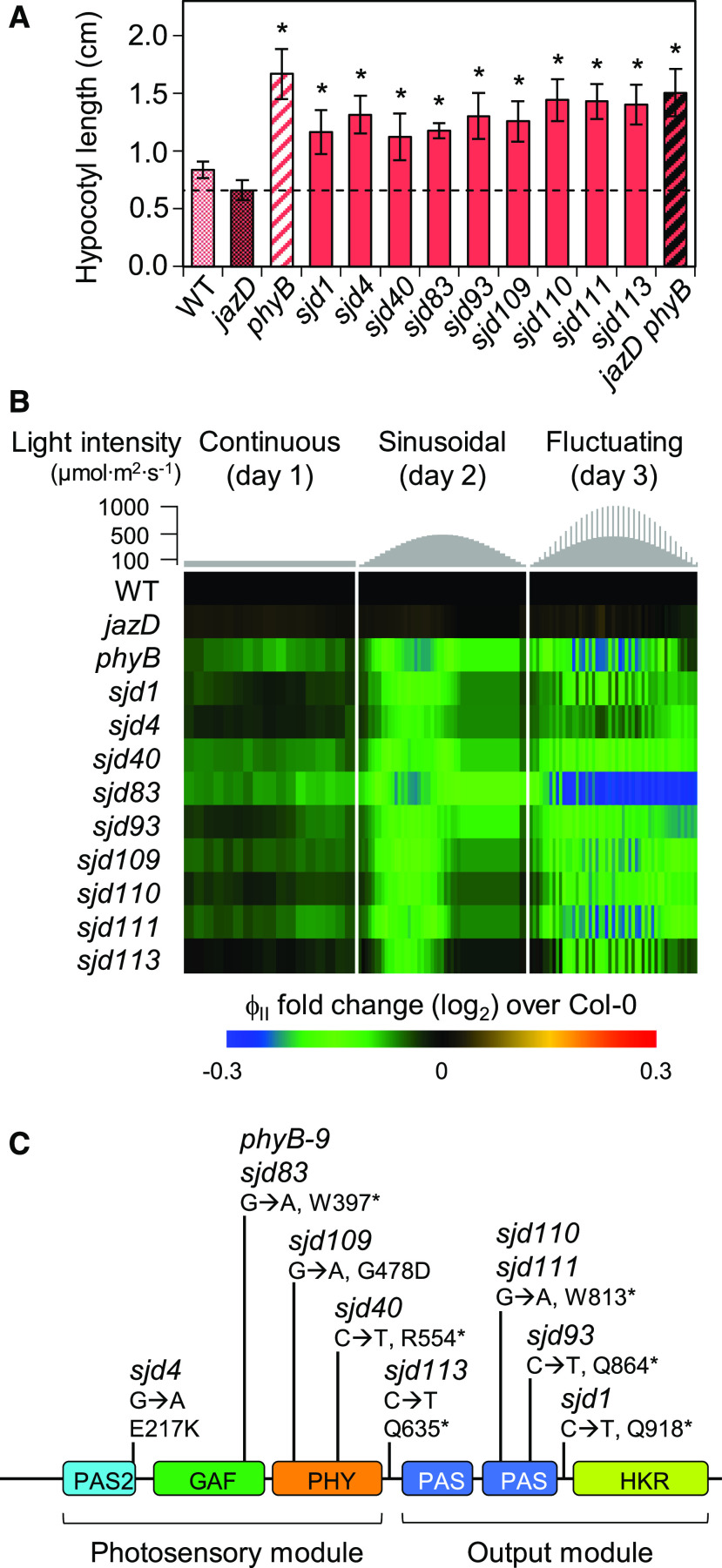
Figure 2.
Long-hypocotyl sjd mutants are impaired in phytochrome B signaling. A, Hypocotyl lengths of long-hypocotyl sjd mutants under monochromatic red light. Seedlings of the indicated genotype were grown for 7 d on LS medium in continuous red light at a fluence rate of 25 μE m−2 s−1. Data points are means ± sd (n = 8–10 plants per genotype). The dashed line indicates the length of jazD hypocotyls. Asterisks denote significant differences at P < 0.05 relative to jazD by Dunnett’s Test. B, Heat map of ΦII, in which chlorophyll fluorescence values for the indicated mutants were normalized to Col-0. Photosynthetic performance was monitored over 3 d of 16 h/d light intensity regimes: constant light (day 1, left); a sinusoidal increase and decrease in light intensity (day 2, middle); and a sinusoidal light regime with higher-intensity pulses (day 3, right). C, Sequencing of the PHYB gene in red-light-insensitive sjd lines identified mutations in all nine mutants. The diagram depicts locations of mutations relative to conserved domains of phyB (colored boxes). Asterisks denote nonsense mutations. One mutant (sjd83) harbors the same G-to-A transition mutation as the phyB-9 mutant allele. The N-terminal photosensory module includes a PAS-2 (Period/Arnt/Single-minded) domain, a GAF (cGMP phosphodiesterase/adenylyl cyclase/FhlA) domain for binding the bilin chromophore, and a PHY domain that stabilizes the photoactivated Pfr state. The C-terminal output module includes two PAS domains and a regulatory His kinase-related (HKR) domain.