Figure 6. Hypoxia and EGF induce EGFR amplification.
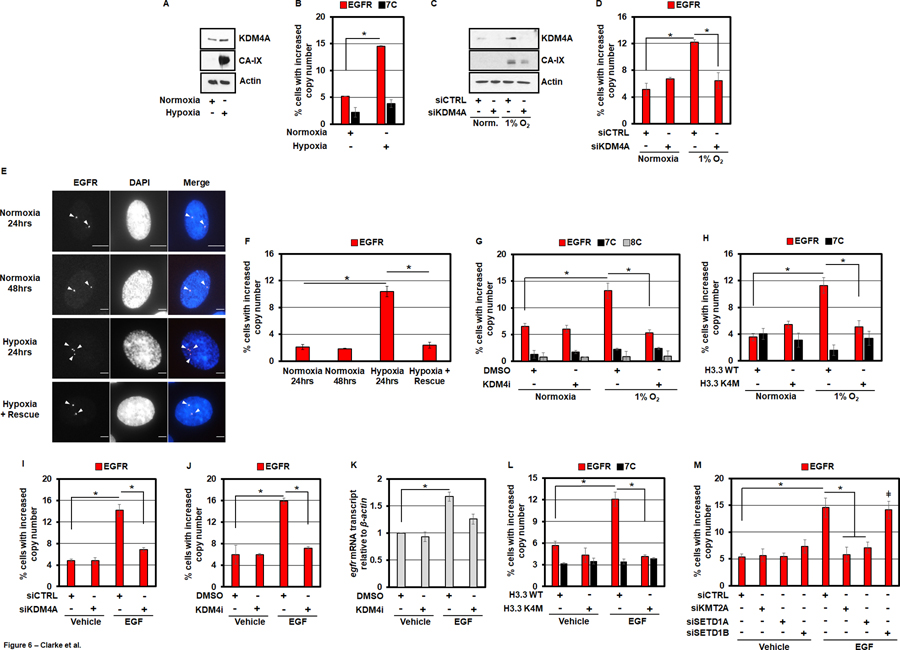
A) KDM4A protein levels increase in RPE cells after being cultured in hypoxia (1% O2) for 24 hours. B) RPE cells cultured in hypoxia for 24 hours have increased EGFR copy gains. C) KDM4A protein levels increase with hypoxia (1% O2 for 24 hours) and are depleted with siKDM4A. D) Hypoxia induces EGFR DNA copy gains in a KDM4A-dependent manner. E) Representative EGFR DNA FISH images of RPE nuclei from cells treated with normoxia (24 and 48 hours), hypoxia (24 hours) or hypoxia (24 hours) and transferred to normoxia (24 hours). EGFR (red) and DAPI (blue) are shown in the merge. F) Hypoxia induced EGFR DNA copy gains are rescued with transfer to normoxia. G) A 24 hour pre-treatment of RPE cells with KDM4i (1nM) completely blocks hypoxia-induced EGFR amplification. H) RPE cells transduced with H3.3 K4M do not exhibit EGFR DNA copy gains when cultured in hypoxia for 24 hours. I) RPE cells treated with 50ng/ml EGF for 24 hours exhibit EGFR amplification that are KDM4A-dependent. J) A 24 hour pre-treatment of RPE cells with KDM4i (1nM) completely blocks EGF-induced EGFR DNA copy gains. K) 50ng/ml EGF for 24 hours increases EGFR transcripts in RPE cells, which is partially KDM4-dependent. L) Following 24 hour stimulation with 50ng/ml EGF, RPE cells transduced with H3.3 K4M do not exhibit increases in EGFR DNA copy number. M) siRNA-mediated depletion of KMT2A and SETD1A blocks EGF-induced EGFR DNA copy gains.
