Figure 1. PAM DANs are necessary for encoding alcohol-associated preference.
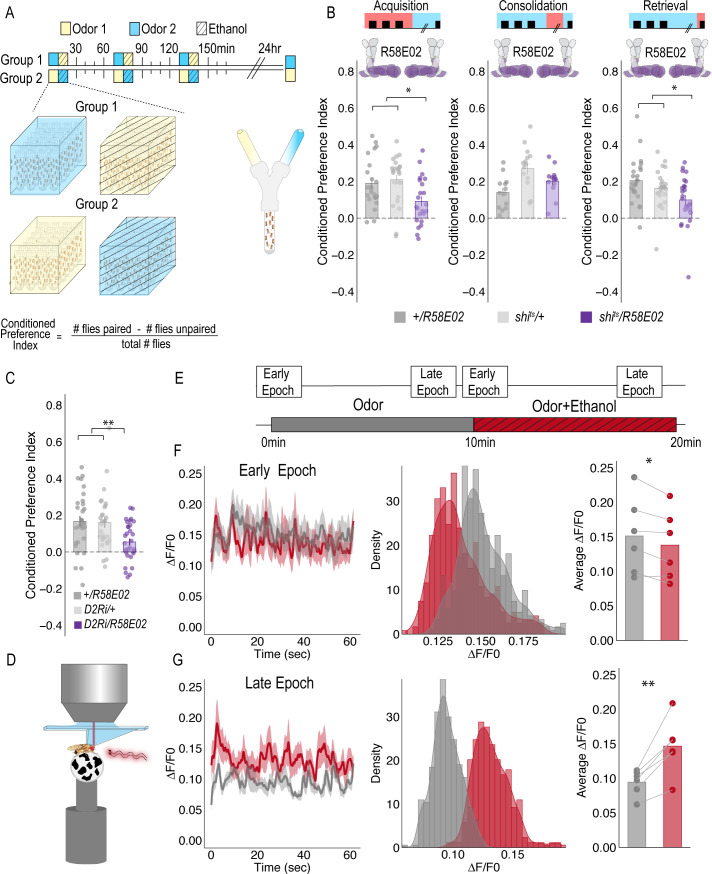
(A) Schematic illustrating odor condition preference paradigm. Vials of 30 flies are presented with three sessions of 10 min of an unpaired odor, followed by 10 min of a paired odor plus intoxicating vaporized ethanol. To control for odor identity, reciprocal controls were used. Flies were tested 24 hr later in a standard Y maze (B) PAM dopaminergic neurons activity is necessary during acquisition (F(2, 66)=5.355, p=0.007) and retrieval (F(2,71)=5.707, p=0.005), but not consolidation. Bar graphs illustrate mean +/- standard error of the mean. Raw data are overlaid on bar graphs. Each dot is an n of 1, which equals approximately 60 flies (30 per odor pairing). One-way ANOVA with Tukey Posthoc was used to compare mean and variance. *p<0.05 (C) RNAi knockdown of D2R within the PAM population targeted using the R58E02 GAL4 driver significantly reduced alcohol-associated preference F(2,89)=6.441, p=0.002. (D) Schematic illustrating calcium imaging paradigm. (E) Flies are exposed to odor followed by odor plus intoxicating vaporized ethanol while resting or walking on a ball. We used the same odor for both conditions so we could better compare circuit dynamics in response to ethanol and control for odor identity. Fluorescence was captured for 61 s recording epochs that were equally spaced by 2 min. (F). Average traces recorded during early odor and odor plus ethanol exposures. Middle panels illustrate the binned ΔF/F0 and highlights a change in calcium dynamics as a consequence of ethanol exposure. Right panels illustrate the average ΔF/F0 for each fly in each condition. Early Epochs of odor plus ethanol had significantly lower signal (F(1,5)=8.705, p=0.03). (G) Average traces recorded during late odor and odor plus ethanol exposures. Middle panels illustrate the binned ΔF/F0 and highlights a change in calcium dynamics as a consequence of ethanol exposure. Right panels illustrate the average ΔF/F0 for each fly in each condition. Late Epochs of odor plus ethanol had significantly higher signal (F(1,5)=24.177, p=0.004). Within Subject Repeated Measures ANOVA was used to compare mean and variance across condition and time. Scale bar = 50 μm *p<0.05 **p<0.01.
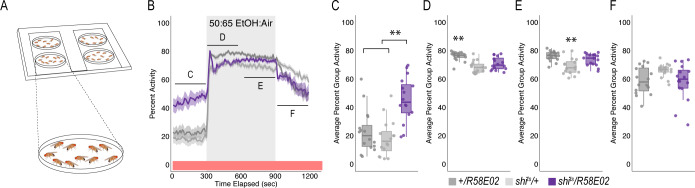
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Although inactivation of PAM neurons increased group flies in an open field arena (n = 15), it did not affect alcohol induced activity suggesting that a decrease in preference is encoded independently from the amount of activity animals exhibit while intoxicated (Figure 1G).
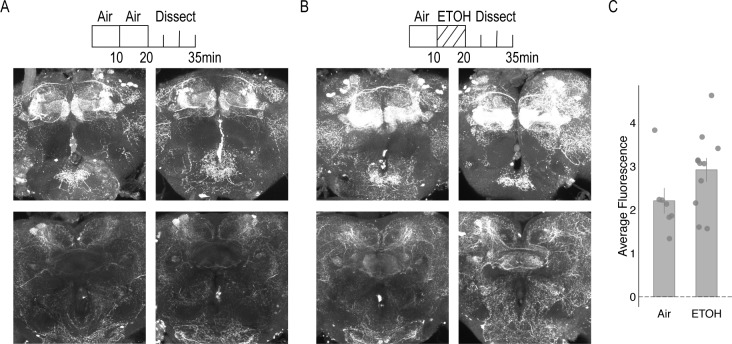
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Dopamine staining within the brain following 10 min of air or 10 min of ethanol.
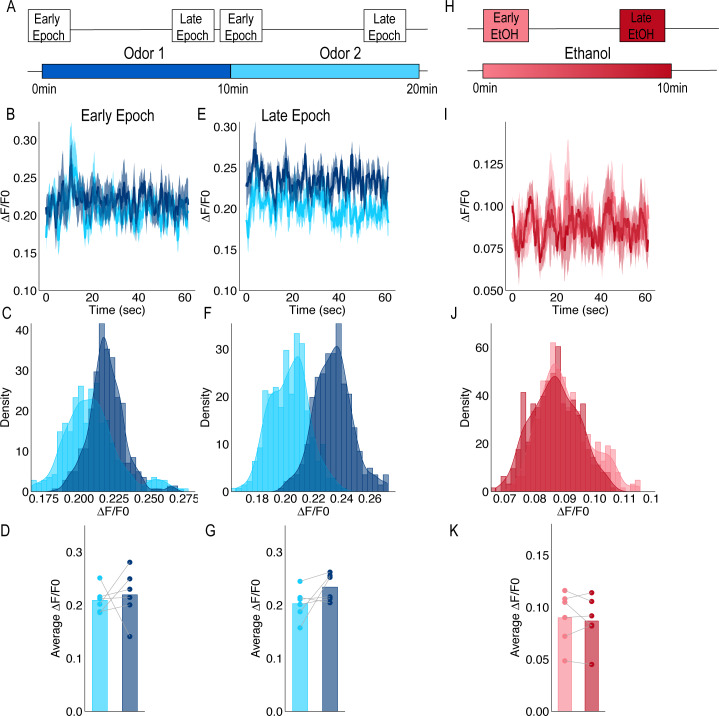
Figure 1—figure supplement 3. Calcium Imaging from terminals of PAM population of DANs in response to odors and ethanol.
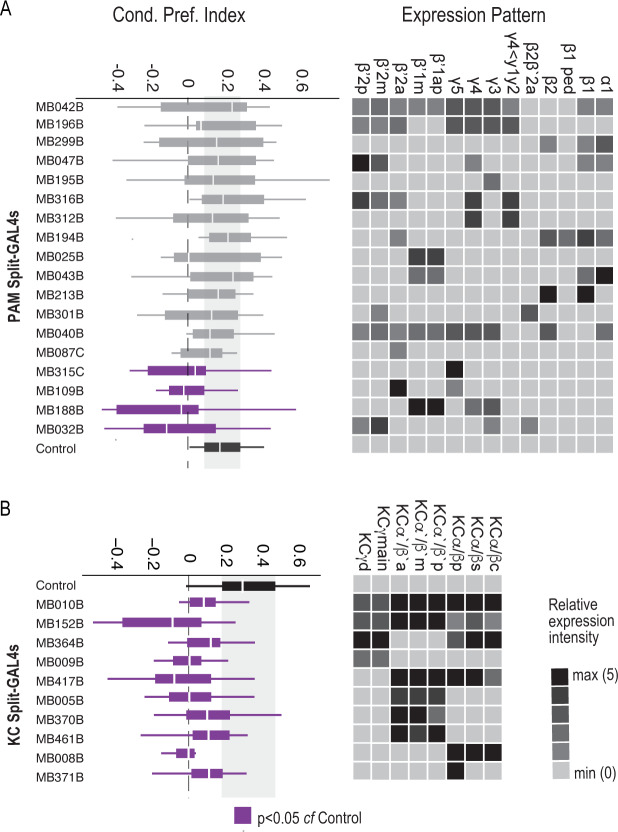
Figure 1—figure supplement 4. Requirement of PAM DANs and Kenyon cells in formation of alcohol-associated preference.
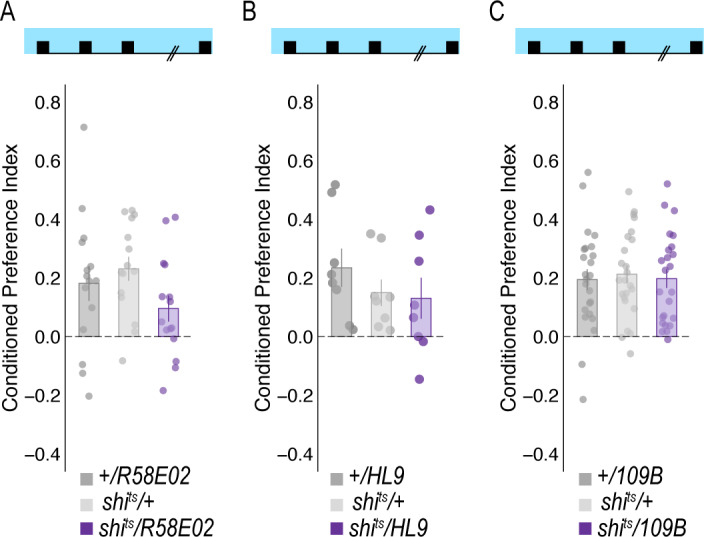
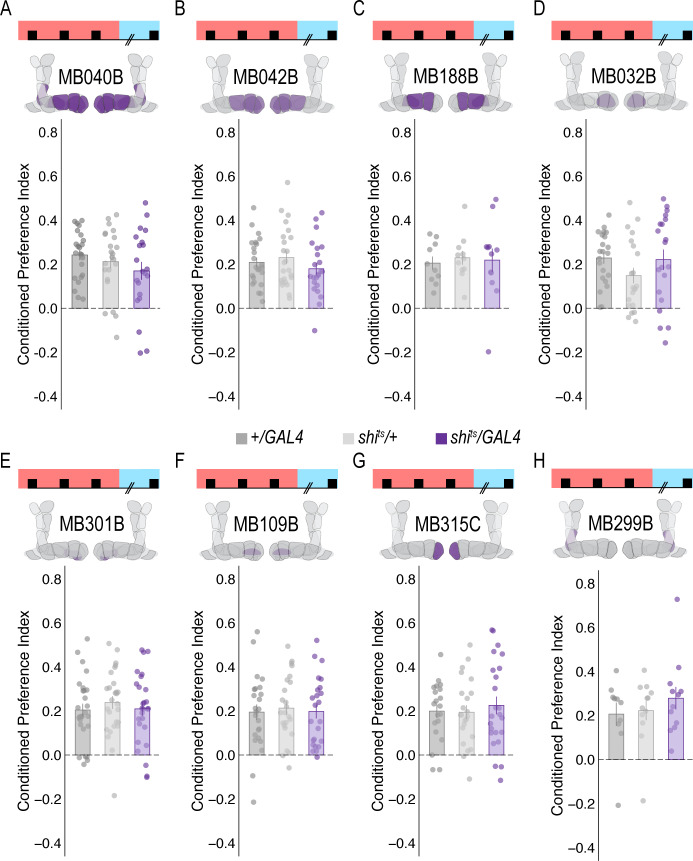
Figure 1—figure supplement 5. Subsets of PAM DANs are dispensable for encoding alcohol-associated preference.
Figure 1—figure supplement 6. Subsets of PAM DANs are required for retrieval, but not acquisition or consolidation.
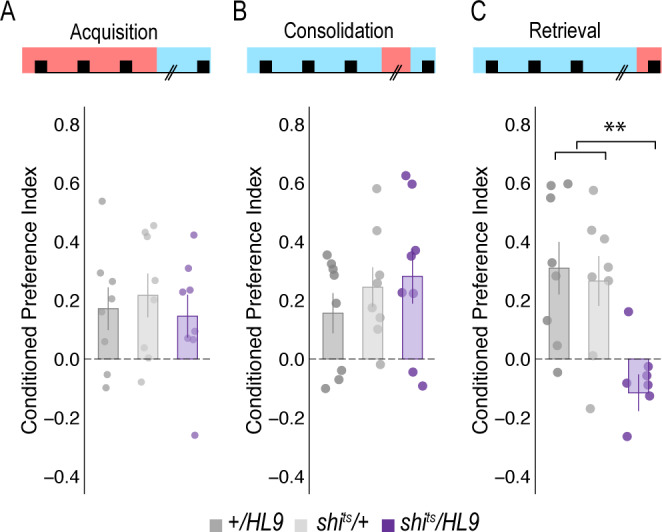
Figure 1—figure supplement 7. mRNA quantification of dopamine receptors (DRs) in all neurons following constitutive expression of DR-RNAi's.
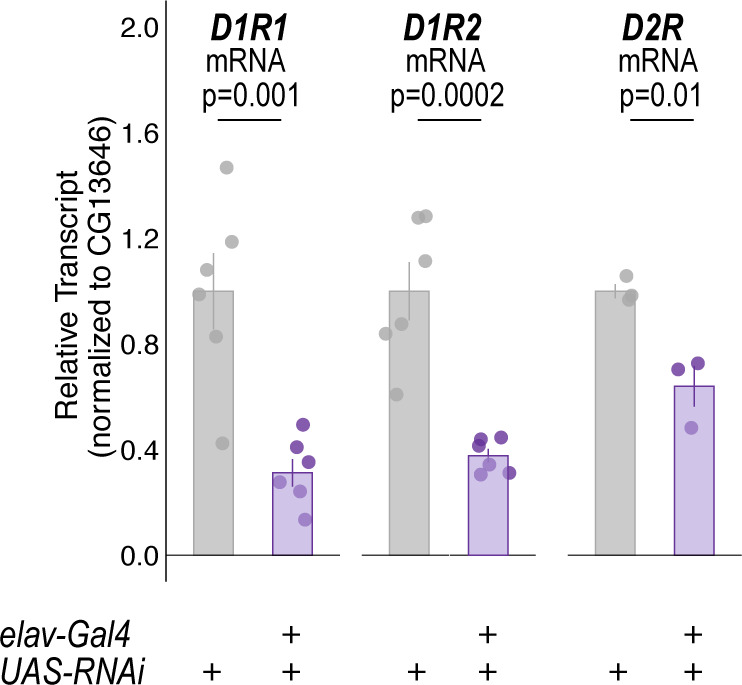
Figure 1—figure supplement 8. Temperature controls for DAN inhibition experiments that showed decreases in retrieval of alcohol associated preference at the restrictive temperature.