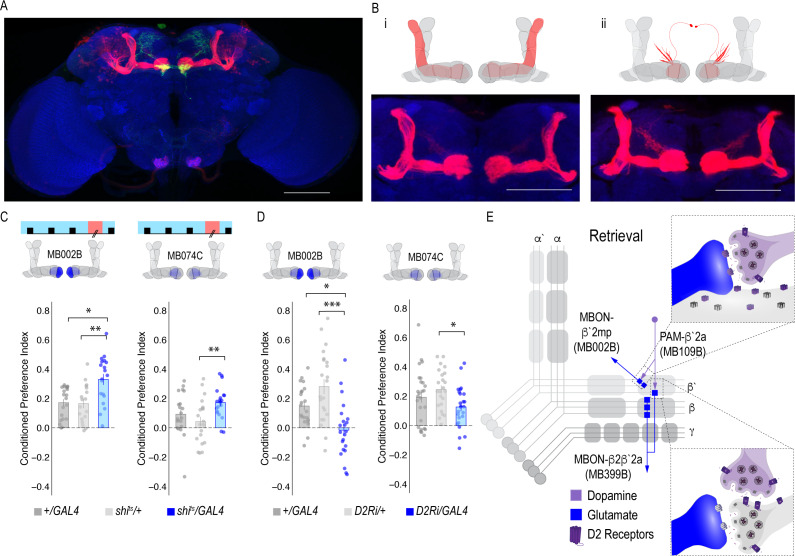
Figure 4. MBON β`2mp glutamatergic neuron is postsynaptic to β`2a PAM DANs and important for memory consolidation.
(A) Representative maximum projection confocal stacks of MB109B > transTango. (B) trans-Tango reveal the α`/β` MB lobe (i) and MBON β`2mp neurons (ii) as postsynaptic to β`2a DANs. (C) Thermogenetic inactivation of MBON β`2mp during consolidation using MB002B significantly increased alcohol reward preference F(2,54) = 9.287, p=0.0003. Thermogenetic inactivation of β`2mp during consolidation using MB074C significantly increased alcohol reward preference relative to UAS controls F(2,71) = 3.51, p=0.04. (D) Knockdown of D2R in MBON β`2mp using MB002B significantly decreased alcohol-associated preference F(2,63)=12.77, p=2.22×10^−05. Knockdown of D2R in MBON β`2mp using MB074C significantly decreased alcohol-associated preference relative to GAL4 controls F(2,71)=3.51, p=0.04. One-way ANOVA with Tukey Posthoc was used to compare mean and variance. Bar graphs illustrate mean +/- standard error of the mean. *p<0.05 **p<0.01 (f) Circuits responsible for encoding alcohol-associated preference during retrieval. Scale bar = 50 μm.
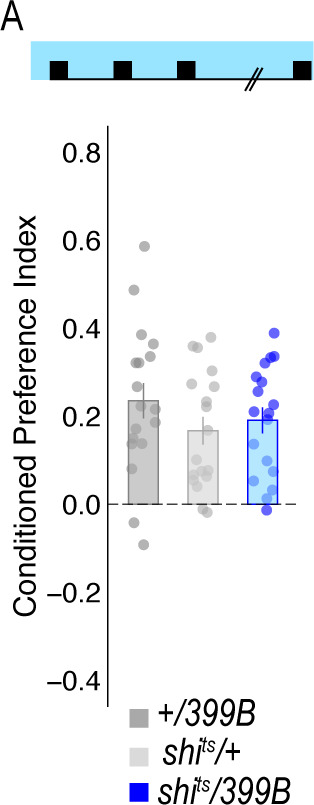
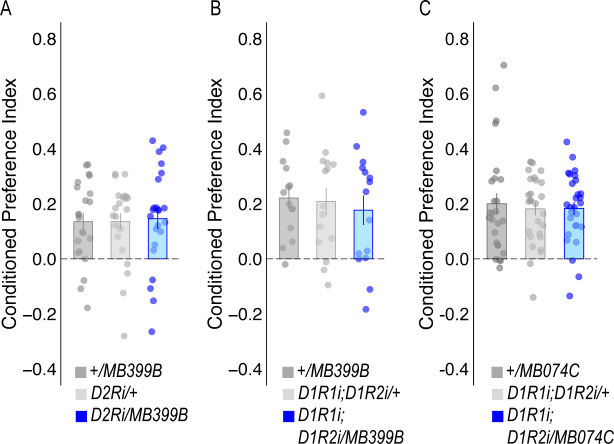
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. RNAi knockdown of dopamine receptors in β`2 MBONs in alcohol-associated preference.
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Temperature controls for lines that showed decreases in retrieval of alcohol-associated preference at a restrictive temperature.