Figure 3: Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor remodeling by Bst1p is important for HsAFP1 internalization and HsAFP1-induced cell death.
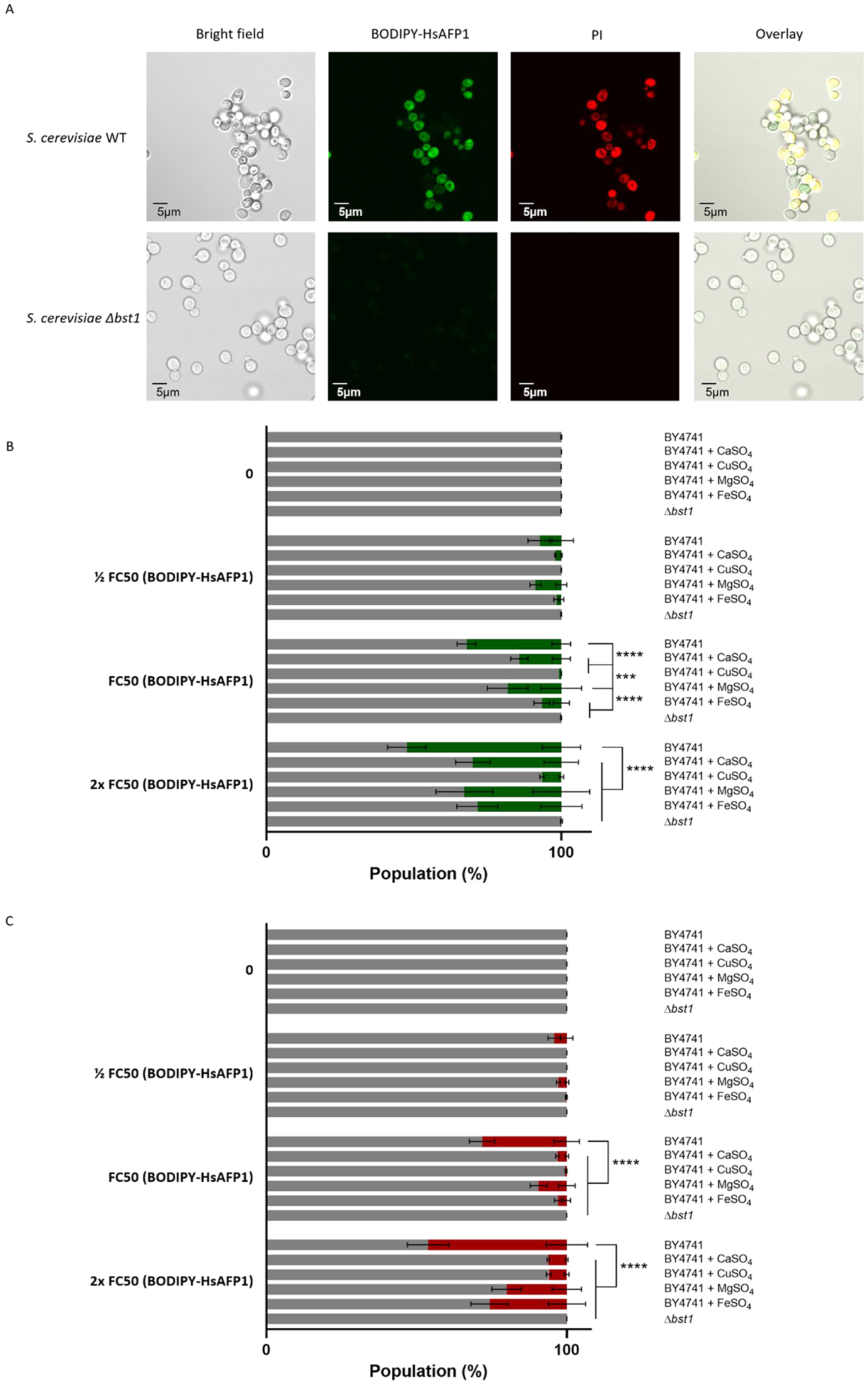
S. cerevisiae WT and Δbst1 mutant cells were treated for 150 minutes in PDB/YPD with 50 mM HEPES pH 7 at 30°C. BODIPY-HsAFP1 and propidium Iodide (PI; 3 μM) were used as markers for peptide internalization and cell death, respectively. (A) Confocal microscope images of S. cerevisiae cells treated with high HsAFP1 doses (10x FC50; 250 μg/mL). Scale bar: 5 μm. (B) Flow cytometry of WT and Δbst1 mutant cells. WT cells are co-administrated with BODIPY-HsAFP1 (1/2 FC50; 12.5 μg/mL, FC50; 25 μg/mL and 2x FC50; 50 μg/mL)and 2 mM CaSO4, 2 mM CuSO4, 2 mM MgSO4 or 2 mM FeSO4. The % of cells that do have BODIPY-HsAFP1 associated with their surface or internalized (green) and the % of cells that do not have BODIPY-HsAFP1 associated with their surface or internalized (grey) is presented. (C) Flow cytometry of WT and Δbst1 mutant cells. WT cells are co-administrated with BODIPY-HsAFP1 (1/2 FC50; 12.5 μg/mL, FC50; 25 μg/mL and 2x FC50; 50 μg/mL) and 2 mM CaSO4, 2 mM CuSO4, 2 mM MgSO4 or 2 mM FeSO4. The % of cells that both have BODIPY-HsAFP1 associated with their surface/internalized and have compromised membranes is presented in red. All other subpopulations are presented in grey, including the % of cells that do not have BODIPY-HsAFP1 internalized or associated with their surface and do not have compromised membranes, the % of cells that do not have BODIPY-HsAFP1 internalized or associated with their surface and do have compromised membranes, and the % of cells that do have BODIPY-HsAFP1 internalized or associated with their surface and do not have compromised membranes. Data are means ± SD for n ≥ 3 independent experiments. To analyze significant differences in the size of the subpopulations, two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey multiple comparison was performed, with *** and **** representing P < 0.001 and P < 0.0001, respectively.
