Figure 5. Effects of CBZ on Bo-786 RCC growth in bone and on bone microenvironment in vivo.
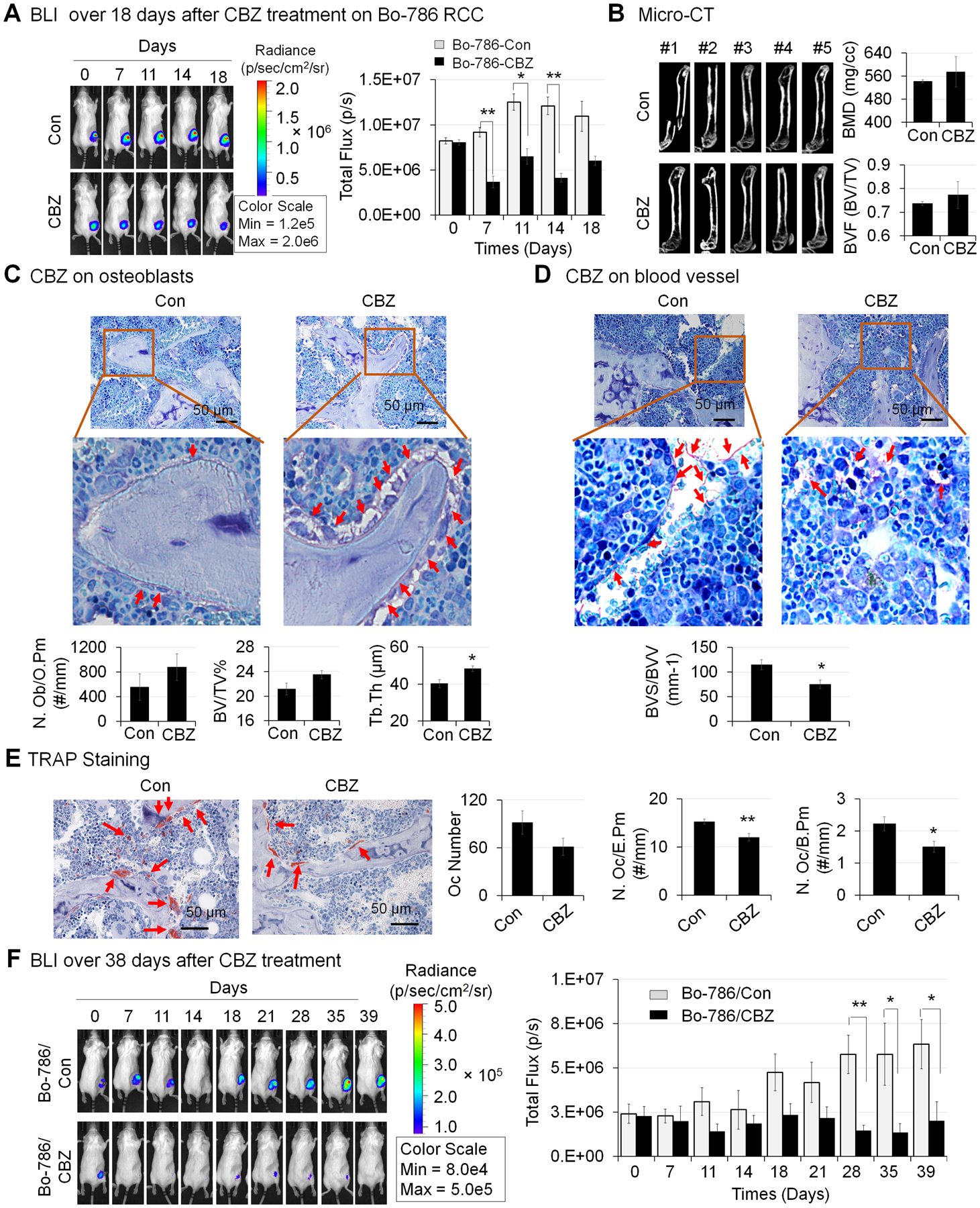
A) The growth of Bo-786 RCC tumor cells in bone over 18 days after initiation of CBZ treatment was monitored by BLI and total flux values were used for BLI quantification. B) Micro-CT analysis of femurs in mice with or without CBZ treatment. Bone mineral density (BMD) and bone volume of whole femur (BVF, BV/TV) was quantified using Microview software. C) Bone histomorphometry analysis of number of osteoblasts per osteoid perimeter (N. Ob/O.Pm), bone volume fraction (BV/TV%) (bone volume/Total volume%) and average trabecular thickness (Tb. Th) on Toluidine Blue stained bone sections. D) Bone histomorphometry analysis of blood vessel volume (BVV) and blood vessel surface (BVS) on Toluidine Blue stained bone sections. E) Bone histomorphometry analysis of number of osteoclasts (Oc Number), number osteoclasts per erosion perimeter (N. Oc/E. Pm), and number of osteoclasts per bone perimeter (N. Oc/B. Pm) on TRAP stained bone sections. F) Growth of Bo-786 RCC tumor cells in bone over 39 days after initiation of CBZ treatment was monitored by BLI and total flux values were used for BLI quantification. *: P < 0.05; **: P < 0.01 as compared to controls.
