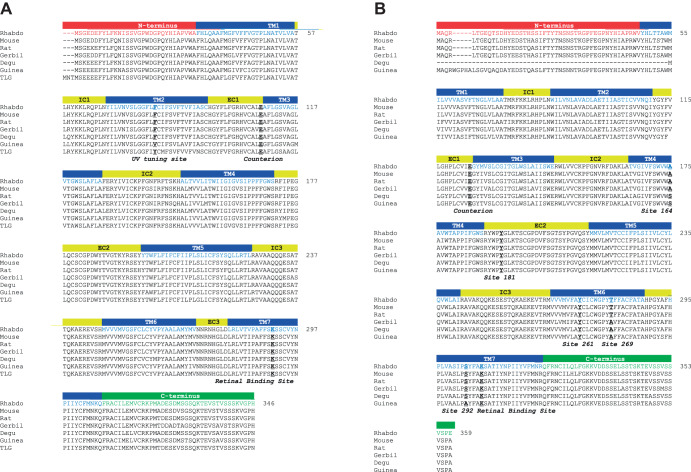
Fig. 1.
Alignment of Rhabdomyspumilio SWS and MWS opsins with sequences of rodent species. (A) SWS opsin of R. pumilio (Rhabdo) and of the following species: Mus musculus (Mouse, NP_031564.1), Rattus norvegicus (Rat, NP_112277.1), Meriones unguiculatus (Gerbil; XP_021517546.1), Octodon degus (Degu; XP_004642783.1), Cavia porcellus (Guinea pig; NP_001166229) and Ictidomys tridecemlineatus [thirteen-lined ground squirrel (TLG); XP_021578083.1]. Rhabdomys pumilio SWS opsin structure is based on mouse SWS1 opsin structure and is shown by labelled coloured bars: TM, transmembrane domain; IC, intracellular loops; EC, extracellular loops. Key sites are shown in bold and underlined: UV tuning site 86, counter-ion site 113, and retinal binding site 296. (B) MWS opsin of R. pumilio and of the following species: M. musculus (NP_032132.1), R. norvegicus (NP_446000.1), M. unguiculatus (XP_021484930.1), O. degus (XP_023561139.1), C. porcellus (NP_001166460.1) and I. tridecemlineatus (AAW29517.1). Rhabdomys pumilio MWS opsin structure is based on mouse MWS opsin structure and is shown by labelled coloured bars as in A. Key sites are shown in bold and underlined: counter-ion site 113; retinal binding site 296; and LWS/MWS spectral tuning sites: 164, 181, 261, 269 and 292. Numbering of key sites is based on bovine rod opsin. All alignments were performed using MAFFT (Katoh and Standley, 2013).