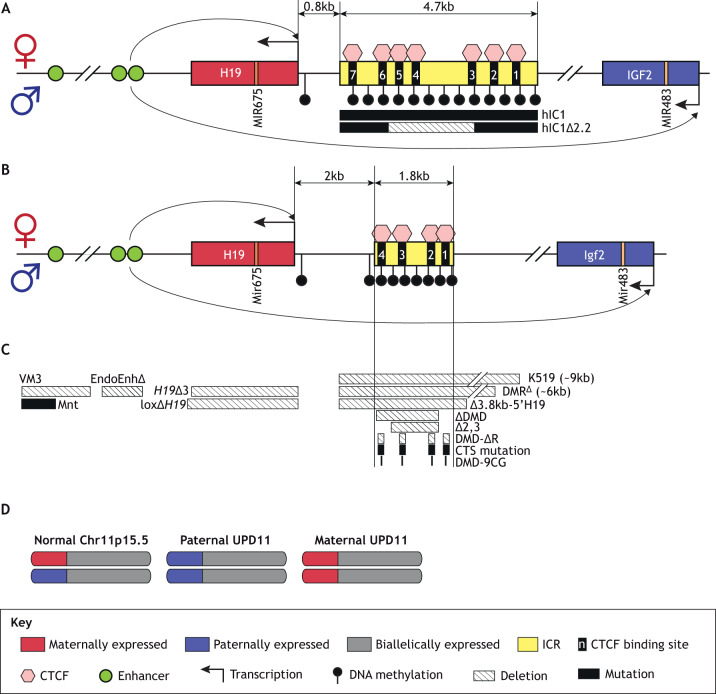
Fig. 1.
H19/IGF2 imprinted locus. (A) Human H19/IGF2 cluster. On the maternal allele, CTCF binds to the unmethylated IC1 and insulates the IGF2 promoter from the downstream enhancers, enabling H19 expression. The methylated paternal IC1 silences the paternal H19 allele and allows IGF2 expression. IGF2 is expressed from multiple promoters. MIR675 is located within the first exon of H19, whereas MIR483 is encoded within the second-to-last intron of IGF2. The BWS-related mutation (hIC1Δ2.2), which was introduced in the humanized IC1 allele in mice, is shown at the bottom of the panel. (B) Mouse H19/Igf2 cluster. The H19/Igf2 ICR is smaller in size and has fewer CTCF binding sites compared to human IC1, but the imprinting mechanism, detailed in A, is conserved between two species. (C) Summary of the mouse models described in this Review. Striped boxes indicate deletions and solid-filled boxes indicate mutations. (D) Simplified depiction of uniparental disomy (UPD). Sizes in kb are approximate and figures are not drawn to scale.