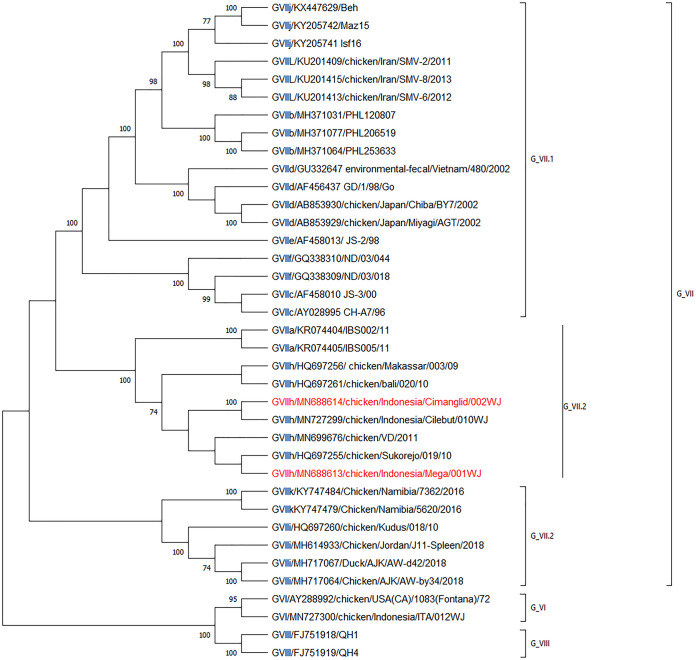
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic analysis based on the full-length fusion protein gene of representative NDV isolates. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the maximum likelihood method and general time-reversible model in MEGA X. The tree with the highest log likelihood (−7,196.50) is shown. The percentage of trees in which the associated taxa clustered together is shown next to the branches. Initial trees for the heuristic search were obtained automatically by applying neighbor-joining and BioNJ algorithms to a matrix of pairwise distances estimated using the maximum composite likelihood (MCL) approach and then selecting the topology with a superior log likelihood value. A discrete gamma distribution was used to model evolutionary rate differences among sites (five categories [+G; parameter, 1.0951]). The rate variation model allowed for some sites to be evolutionarily invariable (+I; 33.02% of sites). This analysis involved 37 nucleotide sequences. Codon positions included were first, second, third, and noncoding. All positions with <95% site coverage were eliminated, i.e., fewer than 5% alignment gaps, missing data, and ambiguous bases were allowed at any position (partial deletion option). There were a total of 1,647 positions in the final data set. The vertical lines show genotype VII, with subgenotypes VII.1 and VII.2, genotype VI, and genotype VIII. The two virulent strains of subgenotype VII.2 in this study are highlighted in red.