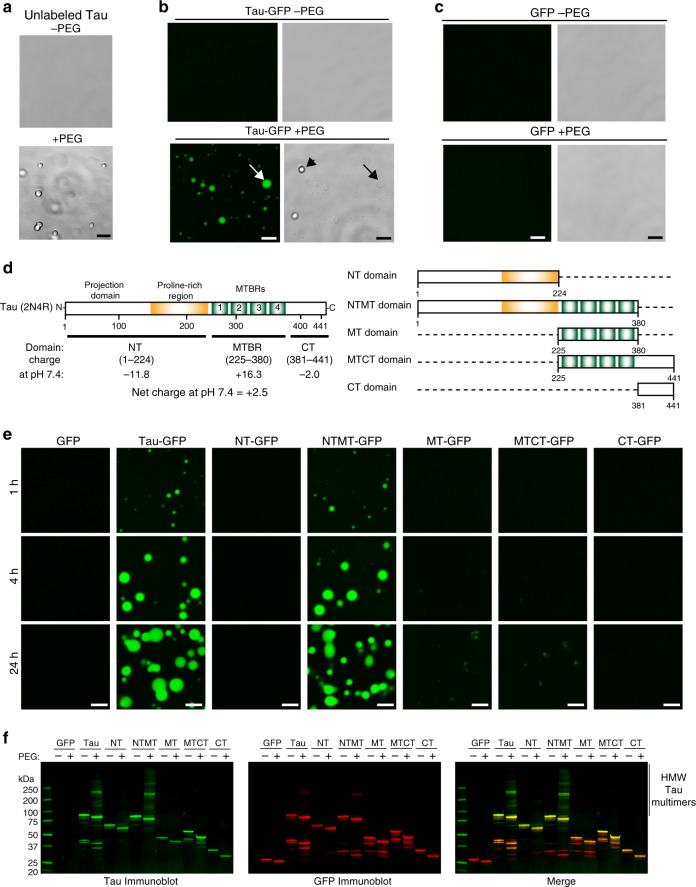
Fig. 1. Tau undergoes liquid–liquid phase separation at physiological concentrations.
a Unlabeled tau (2 μM) does not underdo LLPS without molecular crowding (−PEG), but under crowding conditions (i.e. +PEG at 10%) full-length human tau forms liquid droplets. Scale bar is 5 µm. b Similarly, tau-GFP undergoes phase separation at physiological levels (2 µM tau) to form spherical liquid droplet structures under molecular crowding conditions (+PEG), not in the absence of crowding (−PEG). Tau-GFP liquid droplets initially are formed suspended in solution (black arrowhead), and once settled on the glass slide they wet the surface (white and black arrows). Scale bars are 5 µm. c Recombinant GFP (2 µM) does not form liquid droplets whether PEG is present or not demonstrating that GFP is unlikely to drive tau-GFP LLPS. Scale bars are 5 µm. All experiments performed in LLPS buffer ±10% PEG. d Diagrams of full-length human tau protein illustrating the charges of various domains of the protein at pH 7.4 (overall protein charge is +2.7, note the NT (aa 1–224) = −11.8, and the MT (aa 225–380) = +16.3) and the CT (aa 381–441) = −2.0. The tau domain proteins used in this study also are depicted. e To study which tau domains undergo phase separation, GFP fusion proteins of specific tau domains were used, including the N terminus alone (NT, aa 1–224), the NT through the MTBRs (NTMT, aa 1–380), the MTBRs alone (MT, aa 225–380), the MTBRs through the C terminus (MTCT, aa 225–441) and the CT alone (aa 381–441). The only tau domain construct that exhibited phase separation into liquid droplets at 2 μM was the NTMT protein even after 24 h suggesting the MT and CT are not sufficient for phase separation (representative images of three independent experiments). Notably, the MT alone and MTCT proteins showed a time-dependent (primarily after 24 h) formation of small irregularly shaped structures that did not resemble liquid droplets. As expected GFP alone did not phase separate or form any structures even after 24 h incubation indicating GFP is unlikely to be responsible for the behavior of the tau proteins. f Immunoblotting of GFP and tau domain proteins incubated without (−; i.e. monomeric proteins) or with 10% PEG (+; i.e. liquid droplets) for 4 h shows a clear presence of heat-, reducing- and SDS-stable high molecular weight tau multimers only in full-length tau (tau) and NTMT tau proteins incubated with PEG. Note the other domains did not undergo liquid droplet formation and did not effectively form such multimers confirming these tau species are specifically associated with phase separation. Source data provided in the Source Data file.