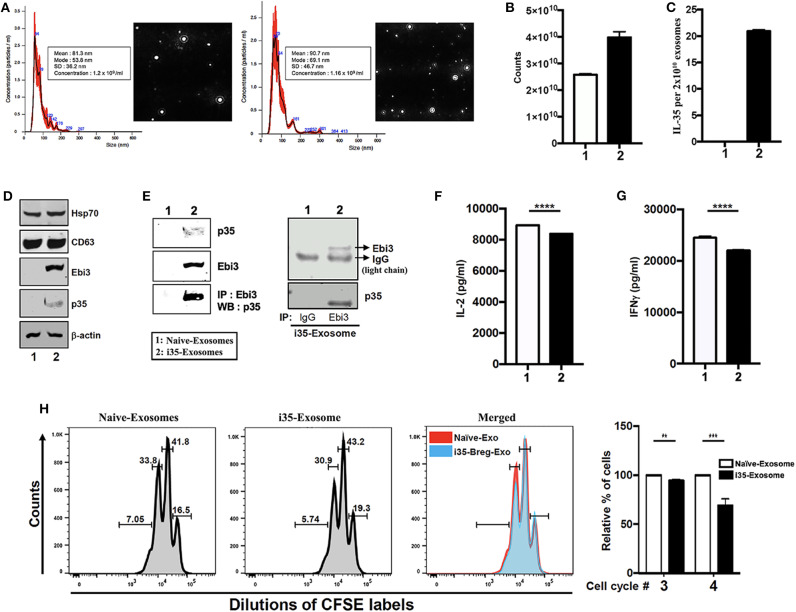
Figure 1.
Breg cells release exosomes that contain the immune suppressive IL-35 cytokine. (A) Purification, characterization, and quantification of exosomes derived from activated B cells that do not produce IL-35 (Naïve-Exosomes) or IL-35-secreting regulatory B cells (i35-Exosomes). Size distribution analysis of exosome samples analyzed by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA). Mean ± SEM of three independent experiments is shown. (B,C) Quantified of exosome released in unstimulated and stimulated B cell cultures by use of the Exosome Quantitation Assay (B) and determination of amounts of IL-35 contained in 2 × 1010 Naïve-Exosomes or i35-Exosomes (n = 6) by ELISA (C). (D) Western blot analysis of exosomal markers (HSP70 and CD63) expressed by exosomes derived from i35-Breg cells (right) or exosomes from B cells that do not produce IL-35 (Naive-Exosomes, left). (E) Lysates derived from Naïve-Exosomes or i35-Exosomes were subjected to immunoprecipitation/Western blot analysis using antibodies specific to Ebi3, p35 or mouse-IgG. (F,G) CD4+ T cells were stimulated in vitro for 3 days in culture medium containing anti-CD3/CD28 Abs and Naïve-Exosomes or i35-Exosomes. Secretion of IL-2 (F) or IFN-γ (G) in the supernatants was detected by ELISA (n = 6). (H) CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 Abs for 4 days under non-polarizing condition in culture medium containing Naïve-Exosomes or i35-Exosomes (20 μg). Effect of Naïve-Exosomes or i35-Exosomes on lymphocyte proliferation was assessed by the CFSE dilution assay. Results represent three independent studies **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.