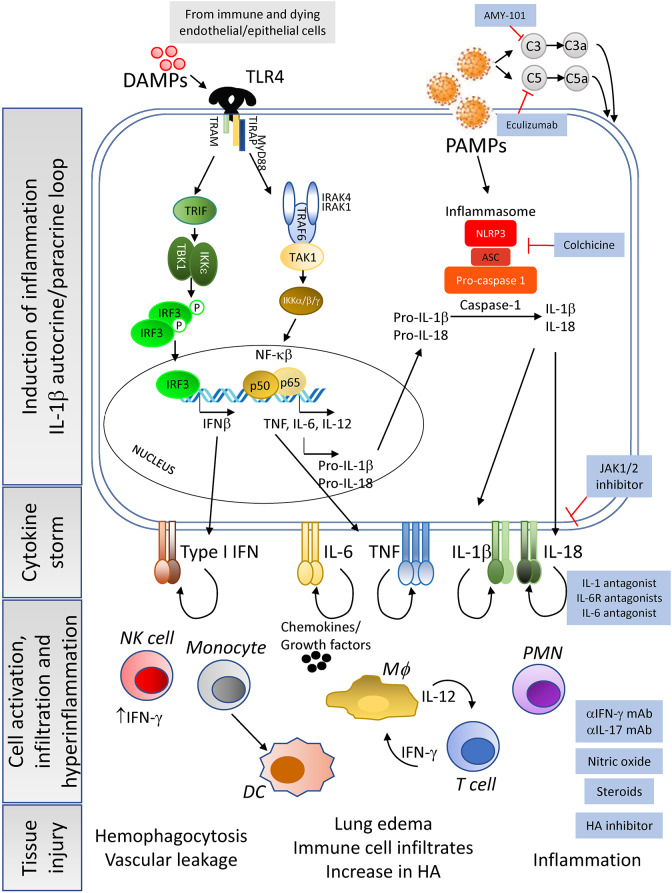
Figure 2.
Cause and consequences of the CRS—Constant exposure to DAMPs from dying infected cells and to high viral titers (pathogen associated molecular patterns, PAMPs) lead to the enhancement of pro-inflammatory cytokine pathways in immune cells and tissue resident cells. In addition, complement activation leads to macrophages activation and cytokine release. Of importance is the induction of the IL-1β autocrine loop, involving the activation of the inflammasome complex that results in high levels of this cytokine being secreted to the extracellular space. Release of IL-1β and subsequent engagement with its receptor will enhance the production of other pro-inflammatory cytokines by the activated cells, leading to a massive release of cytokines, chemokines and growth factors. This cytokine storm creates an inflammatory microenvironment in the tissue, already experiencing elevated inflammation due to the dysregulation of angiotensin II levels, that will feedback into hyperactivation of resident immune cells, as well as mobilization of peripheral immune cells into the tissue. The end result of the dysregulation of the host immune response will be tissue damage and organ failure with the possibility of patient death as severity increases. Pharmacological interventions (blue-background boxes) are being proposed to control or manage the tissue and systemic hyperinflammation detected in moderate and severe cases of COVID-19, by agents that can block the binding of cytokines to their receptors as well as drugs that inhibit the synthesis of hyaluronic acid to prevent pulmonary edema.