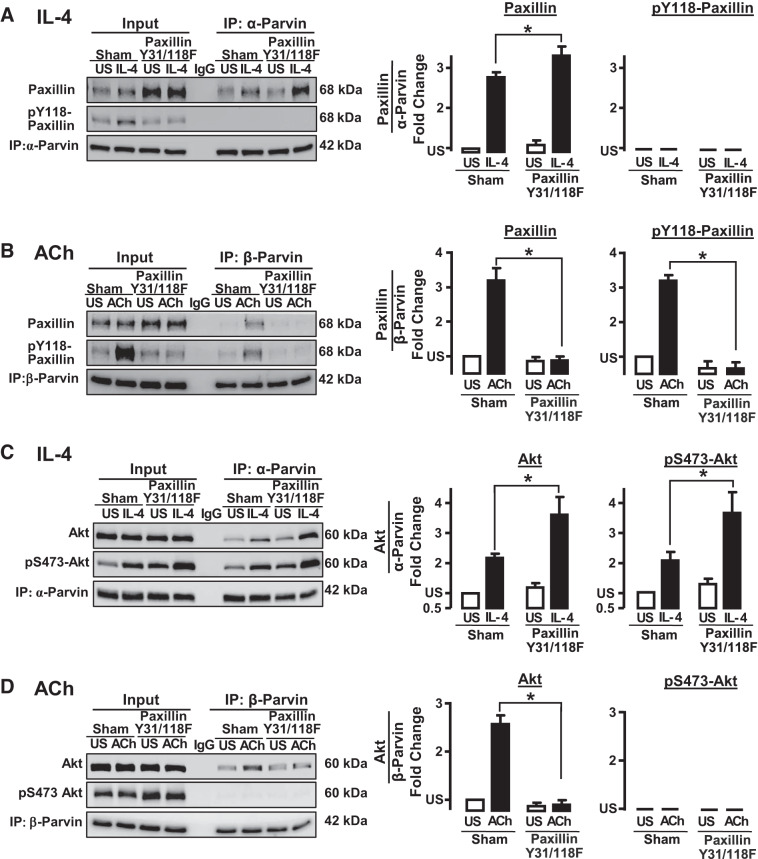
Fig. 11.
Paxillin phosphorylation is required for the interaction of β-parvin with paxillin and Akt in response to ACh. Inhibition of paxillin phosphorylation potentiates the interaction of α-parvin with paxillin and Akt in response to IL-4. A: expression of paxillin Y31/118F in smooth muscle tissues inhibited the ACh-induced increase in endogenous paxillin phosphorylation on Tyr118. The expression of paxillin Y31/Y118F significantly increased the IL-4-induced coimmunoprecipitation (IP) of paxillin with α-parvin immunocomplexes. No phosphorylated paxillin precipitated with α-parvin (n = 5). B: inhibition of paxillin phosphorylation suppresses the coimmunoprecipitation paxillin (n = 6) and phospho-paxillin (n = 4) with β-parvin in response to ACh. C: expression of paxillin Y31/Y118F significantly increased IL-4-induced interactions between α-parvin and Akt (n = 5) and phospho-Akt (n = 4). D: expression of paxillin Y31/Y118F inhibits the coimmunoprecipitation of Akt with β-parvin in ACh-stimulated tissues (n = 5). No phosphorylated Akt precipitated with β-parvin. All values are means ± SE. *Significant difference between Sham-treated tissues and tissues expressing paxillin Y31/118F mutant. Statistical analysis by paired t test. P < 0.05 was considered significant. US, unstimulated.