Figure 1.
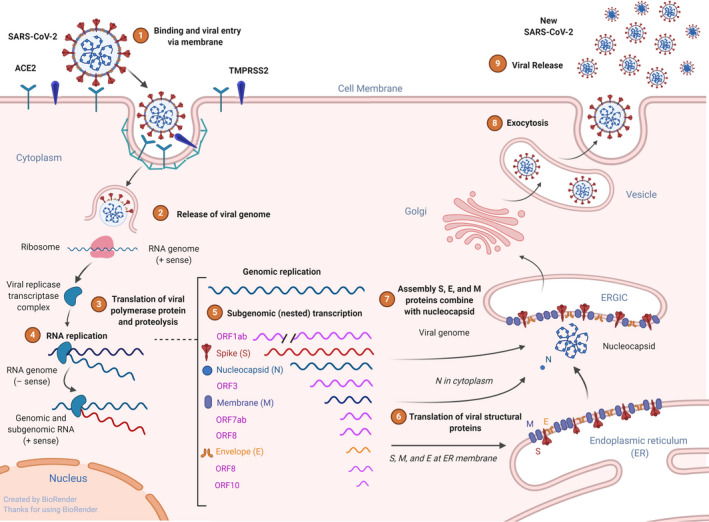
Virus binding, internalization to epithelial cells, and replication. Schematic representation of the genomic and subgenomic organizations of SARS‐CoV and replication. SARS‐CoV‐2 uses receptor ACE2 and transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2) for host cell entry. Following entry to cell cytoplasm, the genomic RNA; the two large open reading frames (ORFs) 1ab are translated into a protein viral transcriptase complex (phosphatase activity and RNA‐dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and a helicase). Replication of the genome involves the synthesis of a full‐length negative‐strand RNA and serves as template for full‐length genomic RNA. After translation, structural proteins are localized to the Golgi intracellular membranes, the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) that is called site of budding. New virions that are assembled full genome RNA release from the cell
