Figure 4.
Mechanisms Underlying the Inversion Association with Diabetes
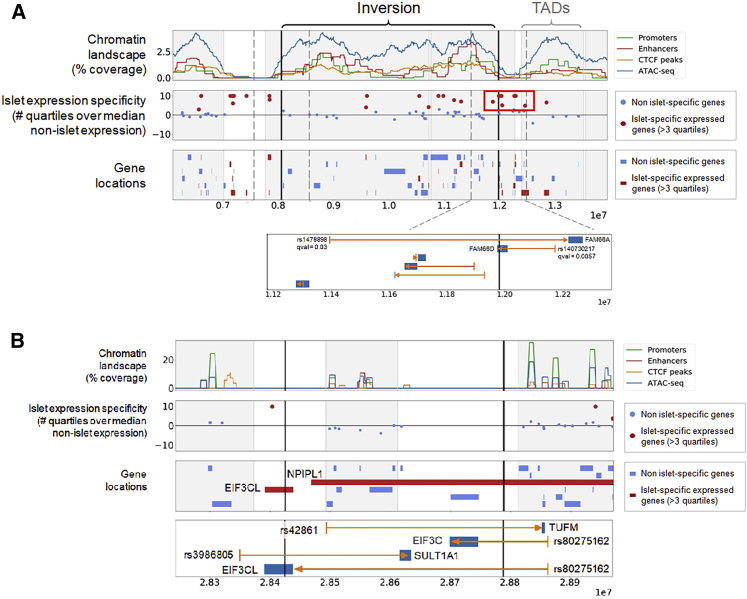
(A) Islet-specific expression of inversion 8p23.1 genes. We observed a cluster of islet-specific genes, mainly lncRNAs, next to the distal inversion breakpoint that could be separated from regulatory elements located inside the inverted region. The bottom panel depicts an eQTLs (rs1478898) of FAM66A disrupted by the inversion distal breakpoint.28FAM66D has its gene body split in two by the inversion, and would also have its promoter separated from its eQLT SNP (rs140730217) by the inversion. This could be the most likely causal candidate.
(B) Same information for the inversion 16p11.2. TUFM and EIF3C have their lead eQTL SNP separated by the inversion breakpoint. There is no evidence in the centiSNP database39 for SNP rs42861 to be causal, suggesting that it should be in LD with the causal variant. This promoter region SNP is located in a segmental duplication block that is closer to TUFM in the inverted haplotypes. Therefore, positional changes made by the inversion can affect TUFM expression by separating the gene from regulatory sequences and subsequently increasing obesity risk.