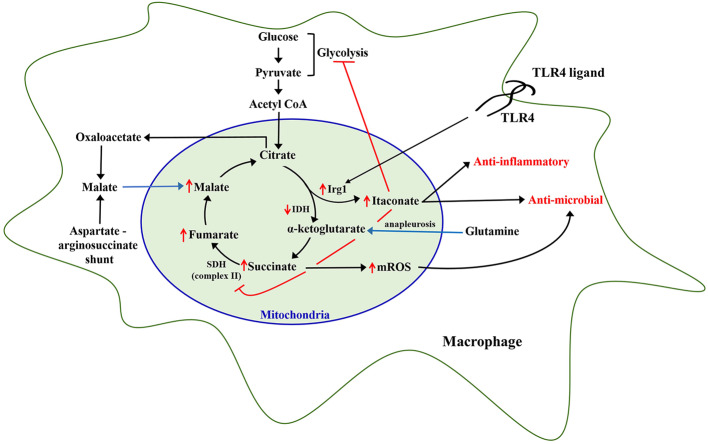
Figure 1.
Metabolic reprogramming of leukocytes. Inflammatory stimulation of leukocytes, specifically monocytes and macrophages, with Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) ligands like lipopolysaccharide, has been shown to rewire mitochondrial metabolic pathways including upregulation of immunoresponsive gene 1 (Irg1) leading to increased itaconate generation, and increased accumulation of other TCA cycle metabolites including succinate, fumarate, malate, and citrate which continue to be replenished via additional pathways including glutamine anapleurosis and aspartate-arginosuccinate shunt. Itaconate produced by Irg1 inhibits succinate dehydrogenase, which causes an increase in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mROS). Itaconate and mROS augment antimicrobial capacity of leukocytes.