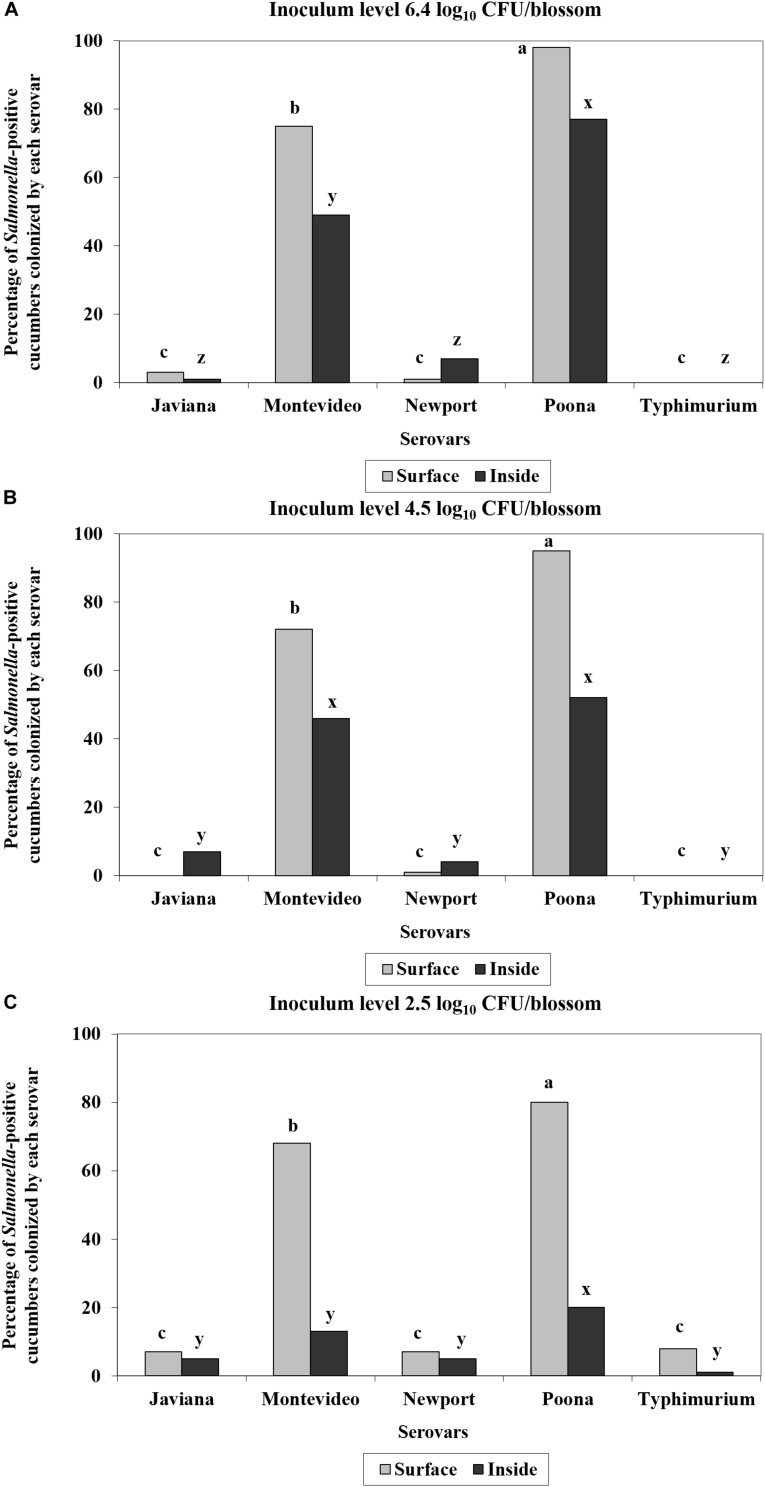
FIGURE 2.
Percentage of each of the five S. enterica serovars identified on the surface (gray) and inside (black) of Salmonella-positive fruits derived from inoculated blossoms. Inoculum levels were ca. 6.4 log10 CFU/blossom (total number of positive fruits, N = 101) (A); ca. 4.5 log10 CFU/blossom (N = 123) (B); or ca. 2.5 log10 CFU/blossom (N = 84) (C). A five-strain cocktail (S. Javiana, Newport, Poona, Montevideo, and Typhimurium) was inoculated onto individually labeled blossoms of cucumber plants. All the cucumber fruits derived from inoculated flowers in the experimental group were harvested and screened for surface and internal populations of Salmonella. Five unique colonies from each XLD-positive plate were randomly chosen for molecular serotyping. Note: multiple serovars were isolated from some of the Salmonella-positive cucumbers. Because there were no significant differences in predominant serotype isolated by cucumber cultivar, all data were combined for statistical analysis. Serovars with different lowercase letters (a, b, c) denote significant differences (P< 0.05) for surface colonization (gray), while serovars with different lowercase letters (x, y, z) denote significant differences (P< 0.05) for inside contamination as determined by Tukey-Kramer honestly significant difference (HSD) testing on two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) results.