Figure 4. Identification of an intragenic autoregulatory SRF enhancer region inhibited by TCF21.
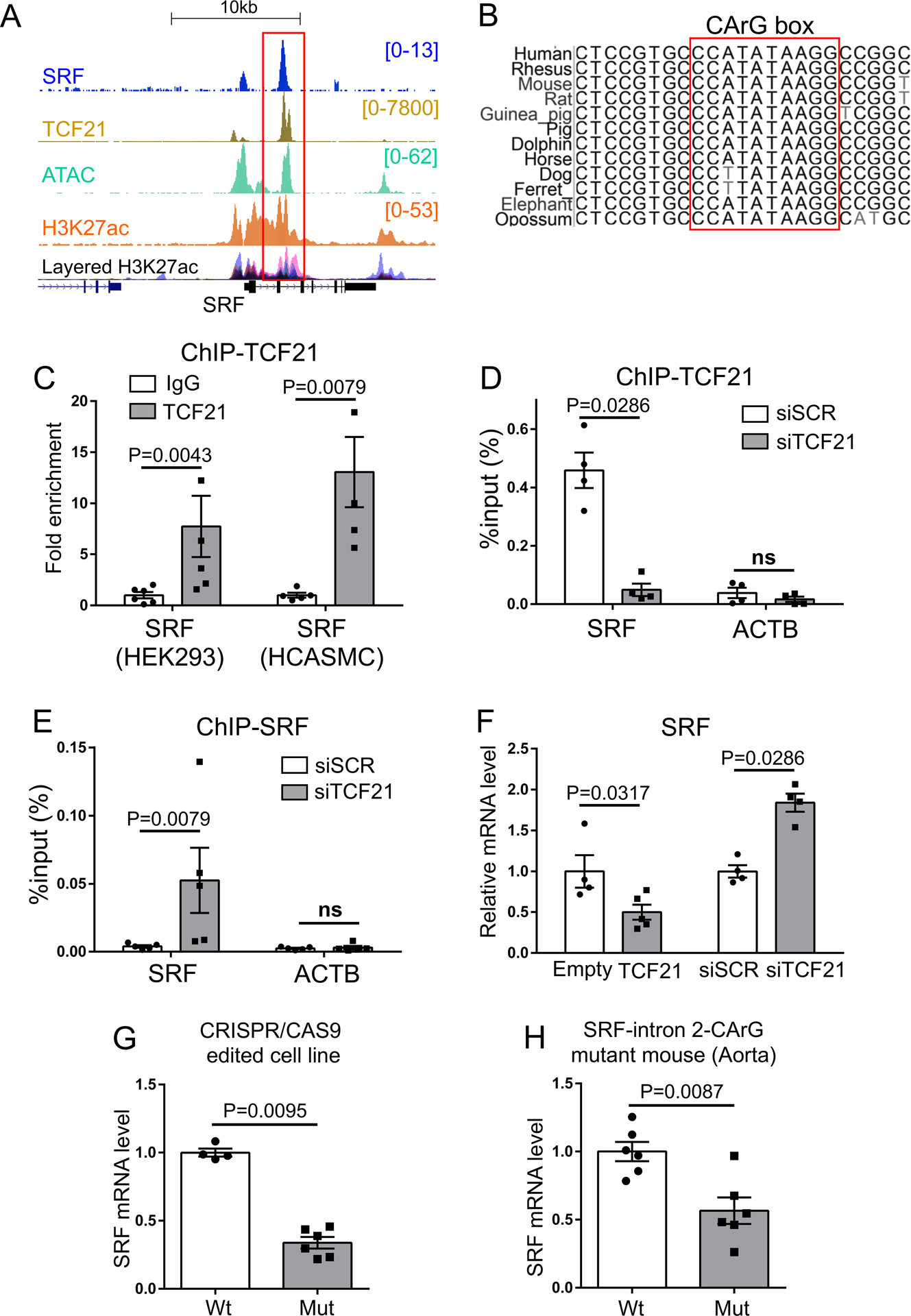
A) Pattern of ChIP-seq mapping of SRF binding as well previously determined TCF21, H3K27ac histone modification and ATAC-seq identification of open chromatin in HCASMC at the human SRF locus. ENCODE H3K27ac data are shown as well. B) Phylogenetic conservation of DNA sequence in the second intron of the SRF enhancer at the CArG box. C) Chromatin immunoprecipitation PCR (ChIP-qPCR) for TCF21 binding at the SRF enhancer in HEK293 overexpressing TCF21 or HCASMC (n=5–6). D) ChIP-qPCR for TCF21 binding (n=4) or E) SRF binding (n=5) at the SRF enhancer in HCASMC treated with siTCF21 or scrambled siRNA (siSCR). ACTB, β-actin transcription start site, was used as a negative control. F) Relative SRF expression level evaluated by qPCR with TCF21 over-expression (TCF21) compared to control (Empty) (n=4–5), and SRF expression level with TCF21 knockdown (siTCF21) or control (siSCR) transfection in HCASMC (n=4). G) SRF expression levels evaluated in wild type (WT) or CRISPR/Cas9 edited mutant CArG box HEK293 cells (Mut) at the SRF enhancer (Wt vs Mut =4 vs 6). H) qPCR analysis of SRF in wild-type (Wt) vs homozygous mutant CArG box (Mut) at the SRF enhancer in mouse aorta (n=6). C-H) Data analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test.
