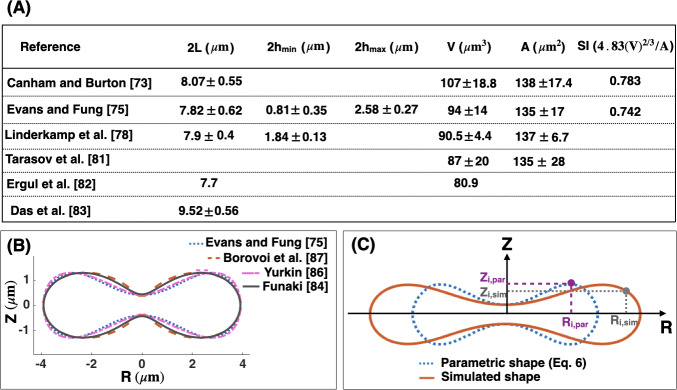
Fig 2. Parametric shape of a RBC.
(A) Dimensions of healthy human RBC from the literature [73,75,78,81–83]. (B) Comparison between the proposed parametric models describing the biconcave morphology of an RBC. There is a close match between the four models for the fixed minimum height of the dimple, maximum height of the rim, and the maximum diameter (C) Discretization scheme of the parametric shape of an RBC (Eq 6) (dotted blue line) and the simulated geometry obtained from our mechanical model (Eqs 4 and 5) (solid red line). Each experimental and simulated shape is discretized into N nodes where i indicates the node index. These nodes are used to compute the total error in the simulated RBC geometry (Eq 8).