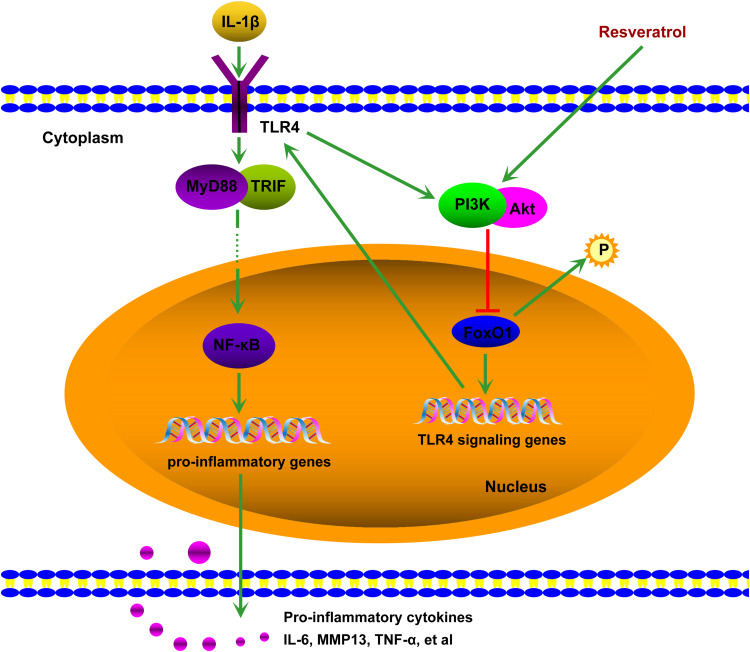
Figure 6.
Schematic description of resveratrol-mediated suppression of inflammation in IL-1β-induced SW1353 cells. IL-1β-upregulated TLR4 expression results in the activation of the TLR4/NF-кB signaling via MyD88-dependent and -independent pathways, which causes translocation of NF-кB into the nucleus resulting in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, MMP13, TNFα, etc. The activation of TLR4 by IL-1β can induce PI3K/Akt phosphorylation, which increases the phosphorylation of FoxO1 and inactivates it. Inactivated FoxO1 reduces the expression of TLR4, establishing a self-limiting mechanism of inflammation. Resveratrol treatment can upregulate PI3K/Akt phosphorylation and inactivate FoxO1, that is resveratrol highlights the self-limiting mechanism by promoting PI3K/Akt activation, thereby down-regulating TLR4/NF-кB pathway and inflammation. ➞, lead to/activate; ⊣, inhibit.