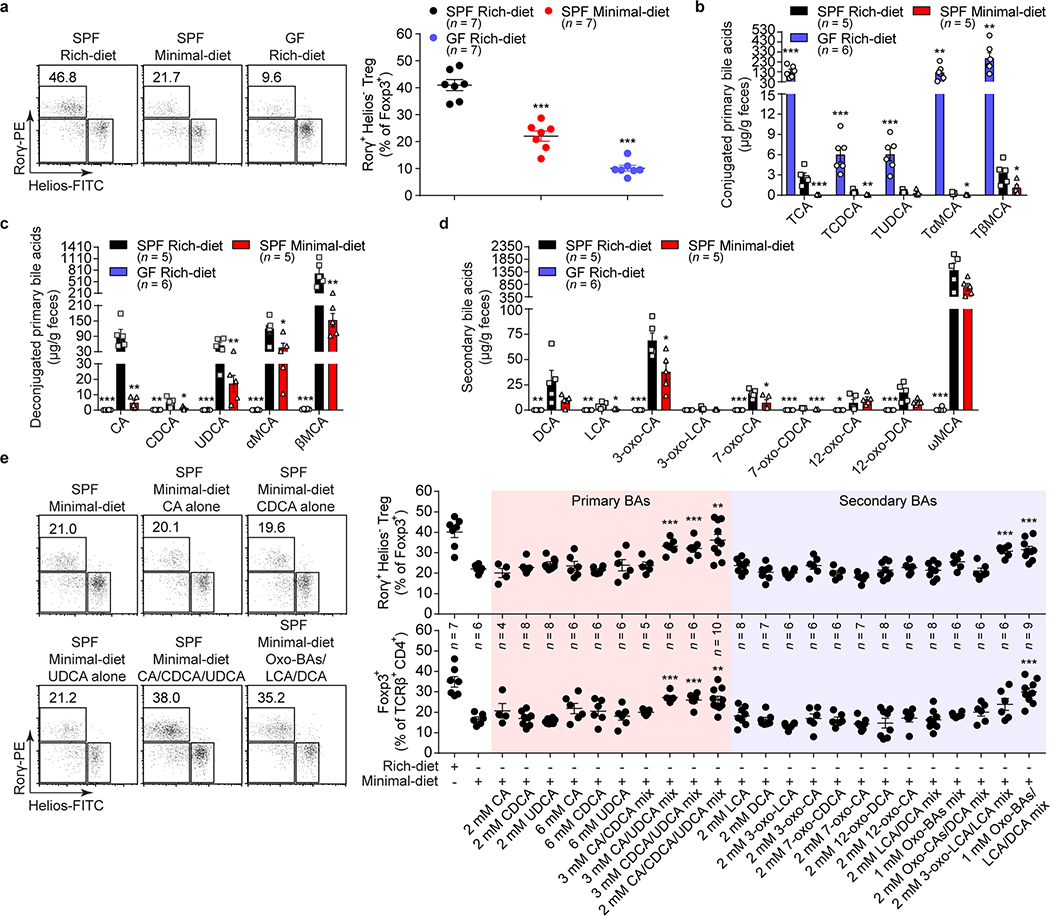
Fig. 1. Gut bile acid metabolites are essential for colonic RORγ+ Treg maintenance.
(a) Beginning at 3 weeks of age, 3 groups of mice were fed special diets for 4 weeks. SPF mice were fed either a nutrient-rich or a minimal diet, and GF mice were fed the nutrient-rich diet. Representative plots and frequencies of RORγ+Helios– in the Foxp3+CD4+TCRβ+ Treg population are shown. (b–d) LC/MS quantitation of fecal conjugated primary BAs (b), deconjugated primary BAs (c), and secondary BAs (d) from groups of mice fed as in a. The BAs determined were cholic acid (CA), chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA), ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), α-muricholic acid (αMCA), β-muricholic acid (βMCA), deoxycholic acid (DCA), lithocholic acid (LCA), 3-oxo-cholic acid (3-oxo-CA), 3-oxo-lithocholic acid (3-oxo-LCA), 7-oxo-cholic acid (7-oxo-CA), 7-oxo-chenodeoxycholic acid (7-oxo-CDCA), 12-oxo-cholic acid (12-oxo-CA), 12-oxo-deoxycholic acid (12-oxo-DCA), ω-muricholic acid (ωMCA), and taurine-conjugated species (TCA, TCDCA, TUDCA, TαMCA, and TβMCA). (e) Three-week-old SPF mice were fed a nutrient-rich diet, a minimal diet, or a minimal diet supplemented with one or more primary or secondary bile acids in drinking water for 4 weeks. Representative plots and frequencies of RORγ+Helios– in the Foxp3+CD4+TCRβ+ Treg population and of Foxp3+ in the CD4+TCRβ+ population are shown. The BAs used in the feed were CA, CDCA, UDCA, DCA, LCA, 3-oxo-CA, 3-oxo-LCA, 7-oxo-CA, 7-oxo-CDCA, 12-oxo-CA, 12-oxo-DCA, and various indicated BA combinations. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments in a-d, Data are pooled from three independent experiments in e. n represents biologically independent animals. Bars indicate mean ± SEM values. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 in one-way analysis of variance followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test.