Figure 1.
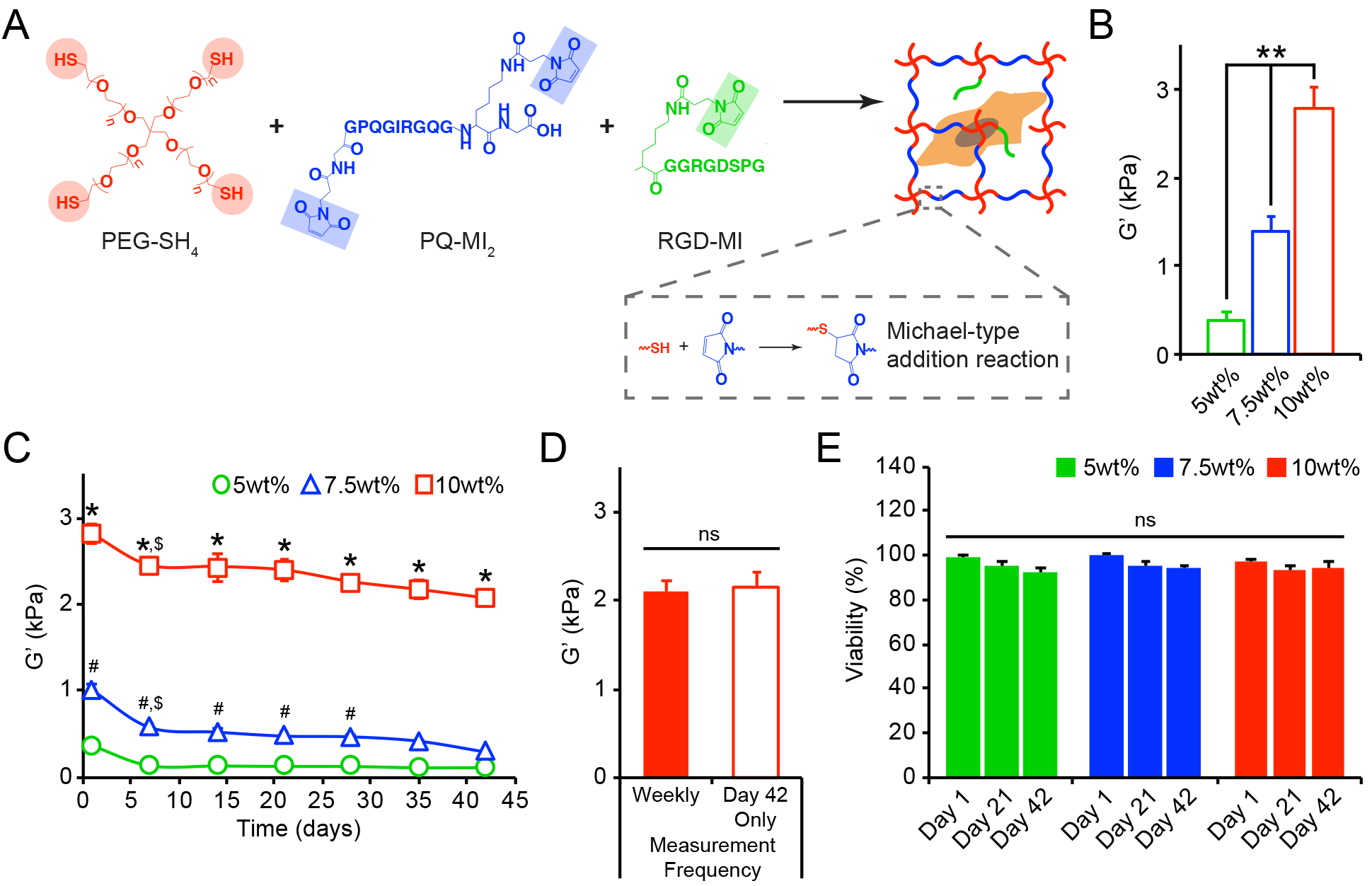
(A) Reaction scheme for enzymatically degradable hydrogel formation. (B) The initial equilibrium storage moduli (G’, kPa), evaluated by oscillatory shear rheology after 24 hrs, significantly increased with increasing wt%. (C) The bulk shear storage moduli (G’, kPa) of acellular 5wt%, 7.5wt%, and 10wt% (w/v%) hydrogels were evaluated once per week by oscillatory shear rheology over 42 days. (D) No differences in the final storage moduli were observed between hydrogels that endured repeated measurements (performed once per week) and those that were measured only once after 42 days of incubation. (E) Cell viability, assessed using live/dead staining, was not compromised by repeated rheological measurements (performed once per week) of cell-laden 5wt%, 7.5wt%, and 10wt% hydrogels. In B-E, data are represented as the mean ± SEM, with n = 3 biological replicates per condition. For B: a one-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey HSD post hoc test, was used to detect statistical significance, **p<0.0001. For C: a two-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey HSD post hoc test, was used to detect statistical significance, *p<0.0001 for 10wt% relative to 5wt% and 7.5wt% at a given time point, #p<0.05 for 7.5wt% relative to 5wt% at a given time point, $p<0.05 for a given time point relative to day 1, within an individual hydrogel formulation. For D-E: no statistical significance (ns) was indicated following (D) a student’s t-test or (E) a two-way ANOVA.
