Figure 3.
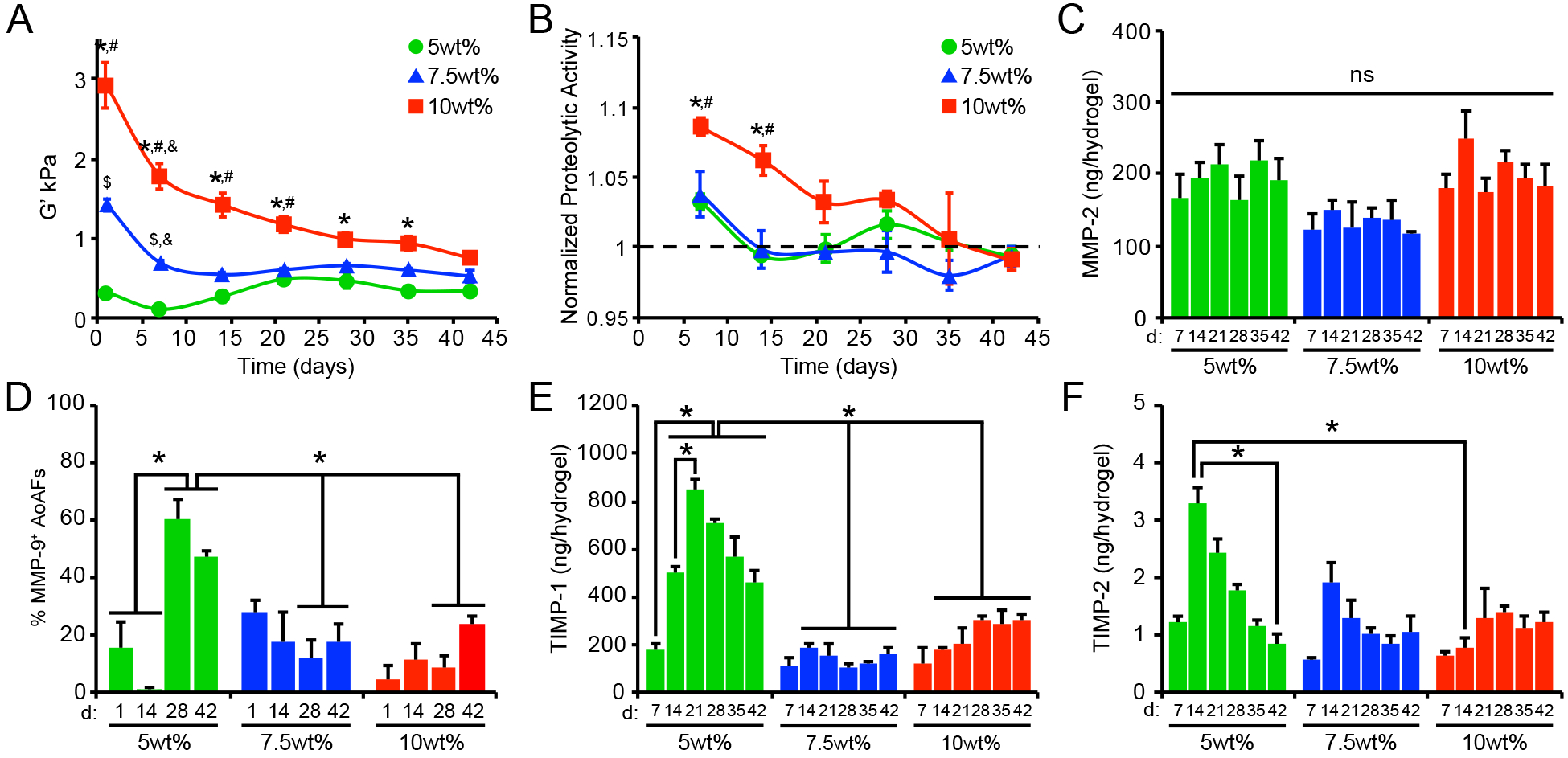
(A) Alterations in swollen storage modulus, measured using oscillatory shear rheology, were observed in AoAF-laden 5wt%, 7.5wt%, and 10wt%, hydrogels over time. (B) Increased proteolytic activity was observed in hydrogels undergoing degradation (i.e. decreased bulk shear storage modulus. Data are mean proteolytic activity relative to acellular hydrogels (dashed line). (C) MMP-2 production by encapsulated AoAFs was similar among hydrogel formulations and over time. (D) Quantification of the percentage of MMP-9-positive cells in AoAF-laden 5wt%, 7.5wt%, and 10wt% hydrogels over the 42 day culture. (E-F) Quantification of the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (E) TIMP-1 and (F) TIMP-2 in the medium collected from AoAF-laden 5wt%, 7.5wt%, and 10wt% hydrogels during the 42 day culture period. Data are mean ± SEM, where in A: n = 6 per condition, in B, D-F: n = 3 biological replicates per condition, and in C: n > 30 cells from 3 images from each of 3 hydrogels per condition. In A-F: a two-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey HSD post hoc test, was used to detect statistical significance. In A-B: *p<0.01 for 10wt% relative to 5wt%, #p<0.05 for 10wt% relative to 7.5wt%, $p<0.05 for 7.5wt% relative to 5wt%, at a given time point; &p<0.01 for a given time point relative to day 1, within an individual hydrogel formulation. In C: no statistical significance (ns) was indicated following a two-way ANOVA. In D-F: *p<0.05 for indicated comparisons.
