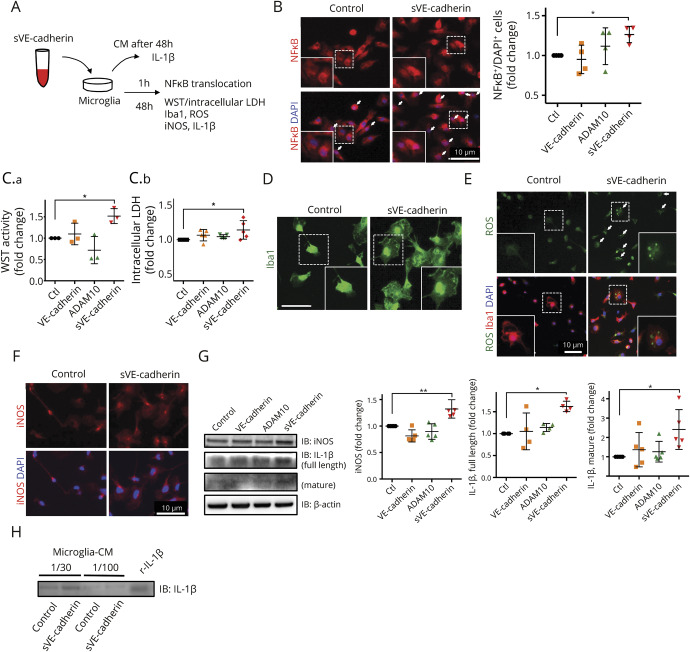
Figure 4. Incubation with soluble vascular endothelial (sVE)-cadherin activates microglia in culture.
(A) Scheme of experimental design of cultured microglia incubated with sVE-cadherin. Conditioned culture media was subjected to Western blot to measure the levels of secreted interleukin (IL)-1β. Immunocytochemistry was performed to assess NFκB translocation, cell soma size, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Western blot of cell lysate was performed to measure the intracellular expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and IL-1β. (B) Quantification of NFκB translocation to nucleus. Nuclear translocation of NFκB is defined as NFκB signal superimposed on DAPI signal. After 1 hour incubation with sVE-cadherin, NFκB translocation to the nucleus is seen in a large number of cells (p = 0.063 with 1-way analysis of variance [ANOVA]; *p < 0.05 with Dunnett multiple comparison, n = 4). (C.a.) Incubation with sVE-cadherin increases microglial metabolism/viability assessed by WST activity (p = 0.003 with 1-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05 with Dunnett multiple comparison, n = 3). (C.b.) There is a trend towards increased intracellular lactate dehydrogenase (p = 0.052 with 1-way ANOVA; *p < 0.05 with Dunnett multiple comparison, n = 5). (D) Iba1 immunofluorescence shows increased microglia cell size after incubation with sVE-cadherin (bar = 10 μm). (E) Immunostaining shows that incubation with sVE-cadherin increases ROS in culturedmicroglia (n = 2). (F, G) Forty-eight hours incubation with sVE-cadherin increases iNOS (F, immunostaining; G, Western blot) and IL-1β (G) in microglia. iNOS: p < 0.001 (**p < 0.01 with Dunnett multiple comparison); full-length IL-1β: p = 0.007; mature IL-1β: p = 0.037 with 1-way ANOVA (*p < 0.05 with Dunnett multiple comparison, n = 5). (H) Western blot indicates that IL-1β is secreted into cell culture media after microglia are incubated with sVEcadherin (n = 2). CM = conditioned culture media; VE-cadherin = vascular endothelial-cadherin.