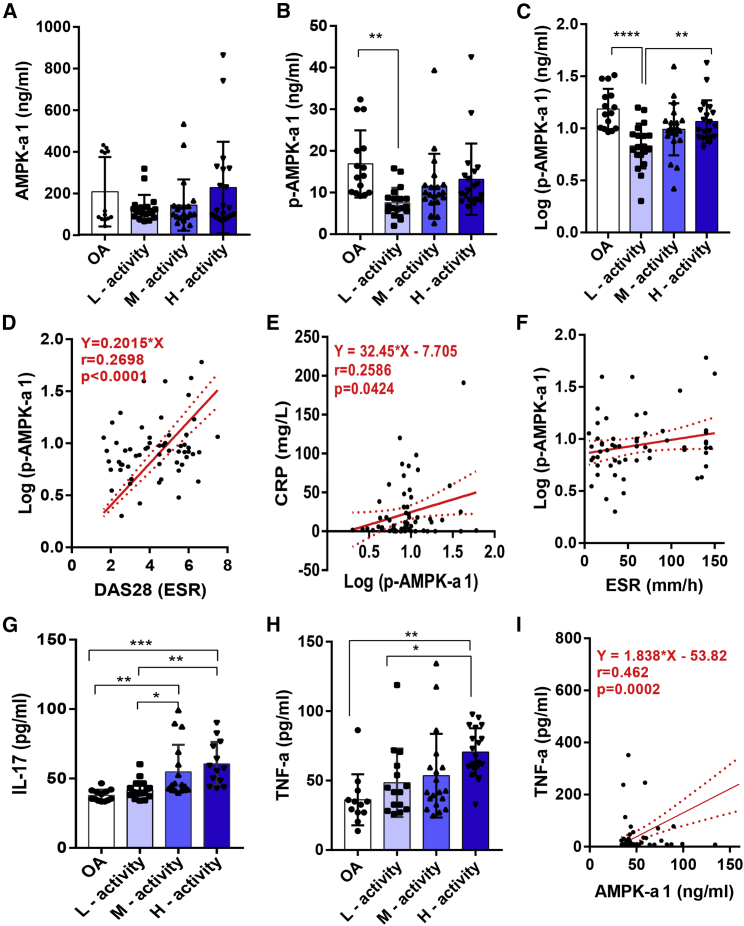
Figure 1.
Expression of Serum AMPK-α1 and p-AMPK-α1 Levels in RA and OA Patients
(A) AMPK-α1 levels between RA (n = 61) and OA (n = 20) patients having moderate to high disease activity were shown, but no statistical significance between groups was observed. (B) Serum p-AMPK-α1 level was higher in OA compared to RA patients having lower disease activity. Log-transformed p-AMPK-α1 values were significantly higher in OA than RA patients having lower disease activity. (C) In RA, patients with higher disease activity had significantly higher levels of log-transformed p-AMPK-α1 levels compared to patients with lower disease activity. (D and E) Log p-AMPK-α1 levels significantly correlated with DAS28 (D) and CRP (E) levels. (F) Correlation with ESR levels was not statistically significant. (G and H) Increased expression of IL-17 (G) and TNF-α (H) was observed in RA than OA patients. (I) Levels of AMPK-α1 moderately correlated with TNF-α levels. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.