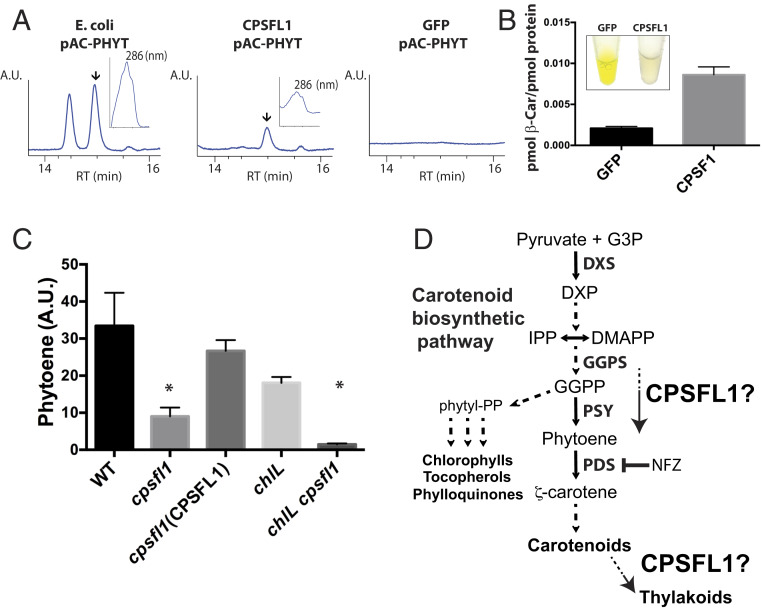
Fig. 6.
Impaired accumulation of phytoene in the cpsfl1 mutant and carotenoid binding by recombinant CPSFL1 protein. HPLC analysis of affinity-purified CPSFL1 and GFP proteins expressed from phytoene- (pAC-PHYTO) and β-carotene– (pAC-BETA) producing E. coli cells. (A) HPLC chromatogram of E. coli whole cells expressing phytoene as well as recombinant purified CPSFL1 and GFP proteins from these cells. Specific pigment peaks are indicated by arrows in the HPLC chromatograms. Inset plots show the absorption spectra for phytoene peak with its absorbance maxima at 286 nm. (B) HPLC β-carotene quantification of recombinant purified CPSFL1 and GFP proteins from E. coli cells overexpressing β-carotene. Inset are pictures of purified proteins at ∼50 mg/mL Error bars represent means ± SD (n = 3). (C) HPLC analysis of phytoene accumulation of NFZ-treated WT, cpsfl1, cpsfl1(CPSFL1) complemented line, chlL, and chlL cpsfl1 double-mutant cells. Error bars represent means ± SD (n = 3). Significantly changed pigments (two-tailed student’s t test; P < 0.05) are marked with asterisks. (D) Schematic diagram showing the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway and the putative roles of CPSFL1 protein in promoting synthesis and/or flux, or transport, of carotenoids (or carotenoid biosynthesis substrates) within the chloroplast. Abbreviations: DMAPP, dimethylallyl pyrophosphate; DXP, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate; DXS, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase; G3P, glyceraldehyde 3-P; GGPS, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; Pyr, pyruvate.