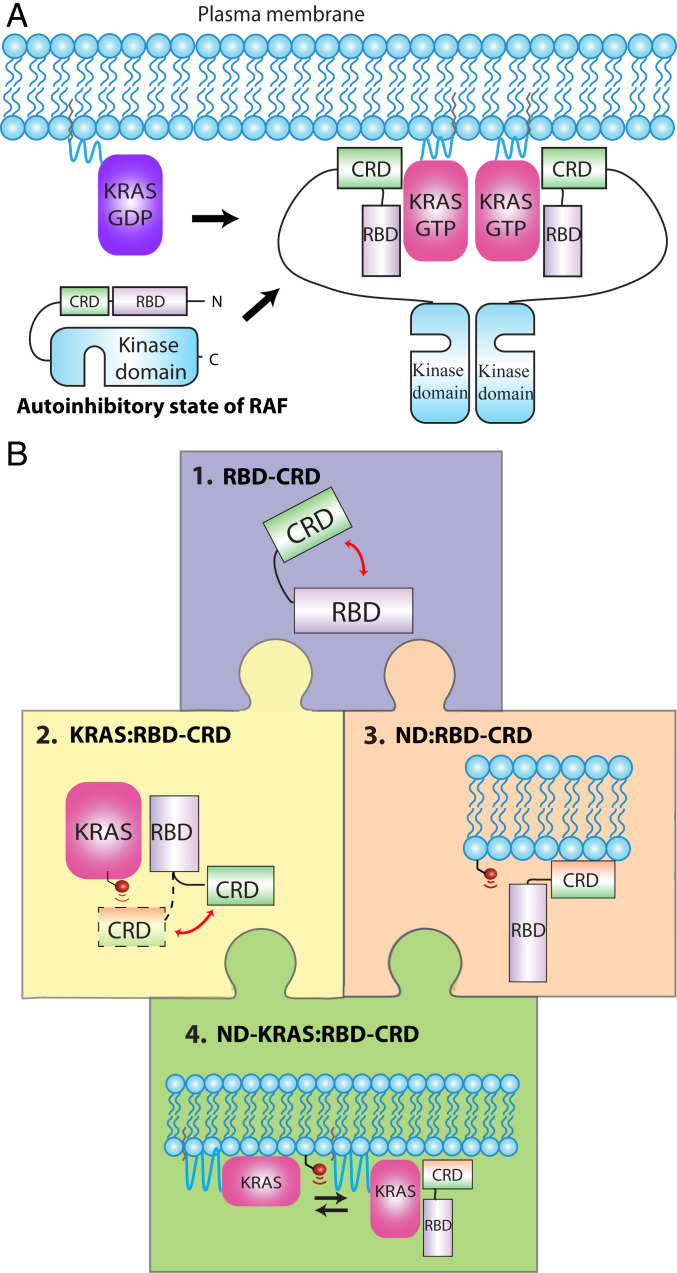
Fig. 1.
Assembly of the KRAS:CRAF complex on the membrane surface and experimental approach for structural studies of bilayer-anchored KRAS in complex with RBD–CRD. (A) assembly of a KRAS:CRAF signaling complex on the membrane upon activation of KRAS. KRAS-GTP binding to the RBD recruits CRAF to the plasma membrane, and the CRD interacts with the surface. This relieves autoinhibition and promotes dimerization of the kinase domain. (B) “Jigsaw puzzle” approach to determining structures of KRAS in complex with RBD–CRD on lipid bilayer. 1, Potential interdomain interactions within the 15-kDa dual RBD and CRD construct were assessed through CSPs (SI Appendix, Figs. S1 and S2). 2, Engagement of RBD–CRD by KRAS in solution was characterized using multiple techniques, including CSP, PRE, and NOEs (Fig. 2 and SI Appendix, Figs. S3–S12). 3, RBD–CRD interactions with the surface of membranes of different lipid composition were characterized using nanodiscs with a PRE-tagged lipid (SI Appendix, Figs. S13–S15). KRAS:membrane interactions were reported previously (21, 22). 4, Finally, the KRAS:RBD–CRD complex was oriented on the membrane surface using lipid-PRE restraints (Figs. 3 and 4 and SI Appendix, Figs. S16–S24).