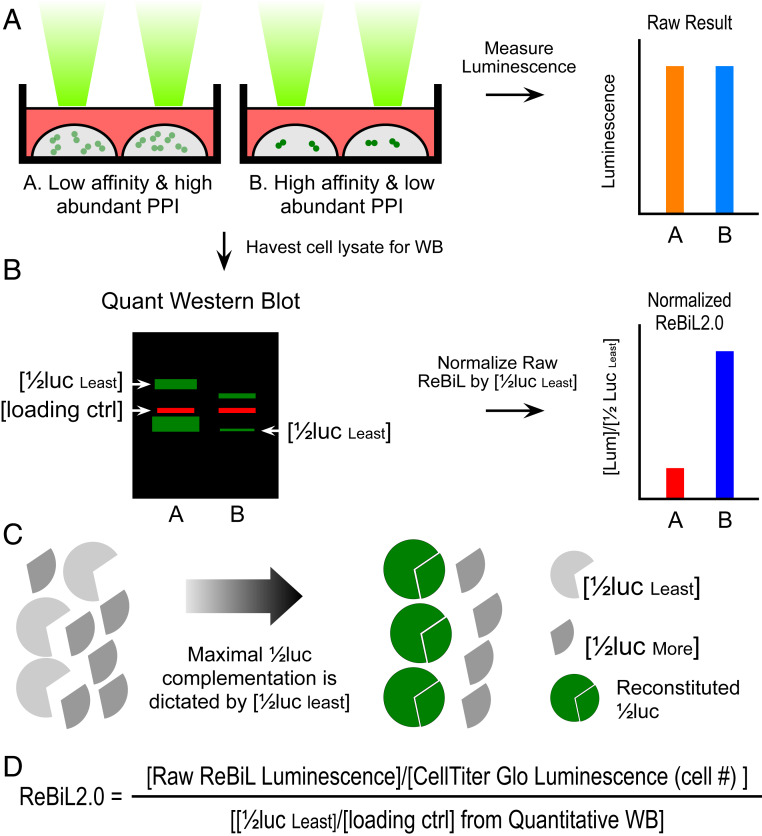
Fig. 1.
Development of ReBiL2.0 assay. (A) The raw luminescent signal reported by the original ReBiL assay does not necessarily reflect the affinity of a pair of PPIs since ReBiL signals depend on both the binding affinity of the interacting proteins and the levels at which they are expressed. That is, signals generated by low-affinity, high-abundance protein interaction (represented by light green dot pairs) may generate luminescent signals similar to those resulting from high-affinity and low-abundance protein interactions (represented by dark green dot pairs). (B) ReBiL2.0 corrects this potential pitfall by normalizing the raw luminescent signal to the expressed level of each 1/2luc fusion protein. The amount of each 1/2luc fusion protein and loading control (actin) were quantified by probing Western blots with anti-HA and anti-actin antibodies simultaneously using the LI-COR Odyssey two-channel system (Left). (C) Although controlled by the same TRE (tetracycline response element) bidirectional promoter, 1/2luc fusion proteins are not always expressed in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio. Thus, the maximal luminescent output generated by reconstituted split-luciferase is determined by the least abundant 1/2luc fusion [1/2luc least] when the 1/2luc fusions are not expressed in 1:1 stoichiometry. Since each 1/2luc fusion protein contains a single copy of an HA-epitope tag in the linker region (Fig. 2A), quantitative Western blotting with an anti-HA antibody enables accurate determination of their relative expression levels as shown in B. (D) ReBiL 2.0 formula. The raw ReBiL signal [Raw ReBiL Luminescence] is measured by a luminometer. Then, the relative viable cell number in each sample is measured using CellTiter Glo [CellTiter Glo Luminescence (Cell #)] upon termination of the ReBiL2.0 assay. The [1/2lucleast] and [loading ctrl] were determined by the corresponding band intensities in Western blots using the LI-COR Odyssey system (SI Appendix, Fig. S2I and Table S3).