Figure. Inborn errors of IL-17 immunity in patients with isolated or syndromic CMCD.
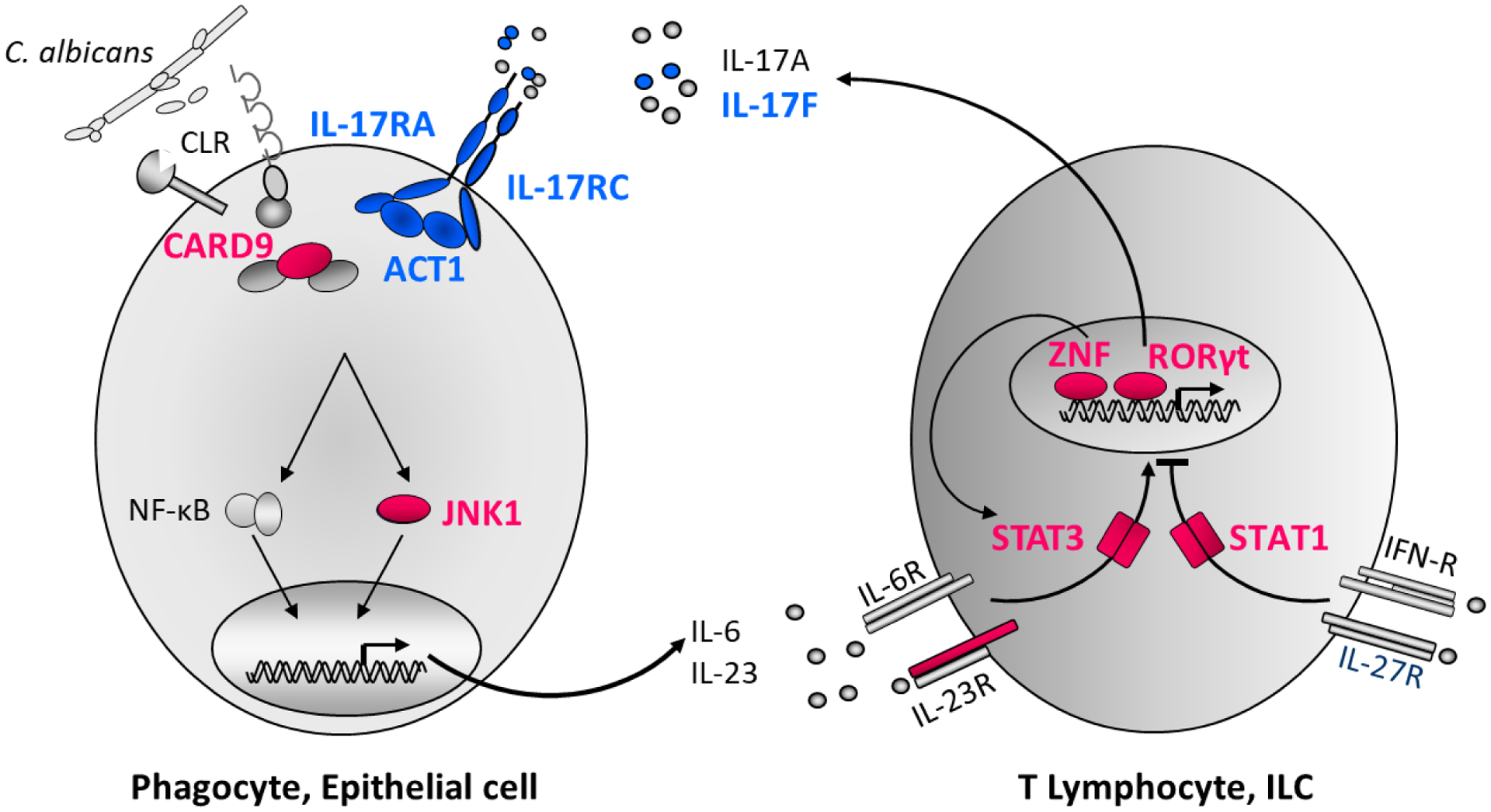
Schematic representation of IL-17A/F immunity and cooperation between cells recognizing C. albicans and responding to IL-17A/F (phagocytes and epithelial cells), and cells producing IL-17A/F (T and innate lymphocytes). Human IL-17A/F immunity is crucial for protective mucocutaneous immunity against C. albicans. Proteins for which mutations in the corresponding genes underlie CMCD are shown in blue or red. Monoallelic LOF mutations of IL17F and of MAPK8, and bi-allelic LOF mutations of IL17RA, IL17RC and ACT1 impair IL-17A and IL-17F immunity (via IL-17RA/IL-17RC). Bi-allelic LOF mutations of IL12RB1, RORC, ZNF341, monoallelic LOF mutations of STAT3 and monoallelic GOF mutations of STAT1 impair IL-17A/F production. Mutations of IL17F, IL17RA, IL17RC and ACT1 underlie isolated CMCD (blue), whereas mutations of IL12RB1, STAT1, STAT3, ZNF341 and RORC underlie syndromic CMCD (in red).
