Figure 1.
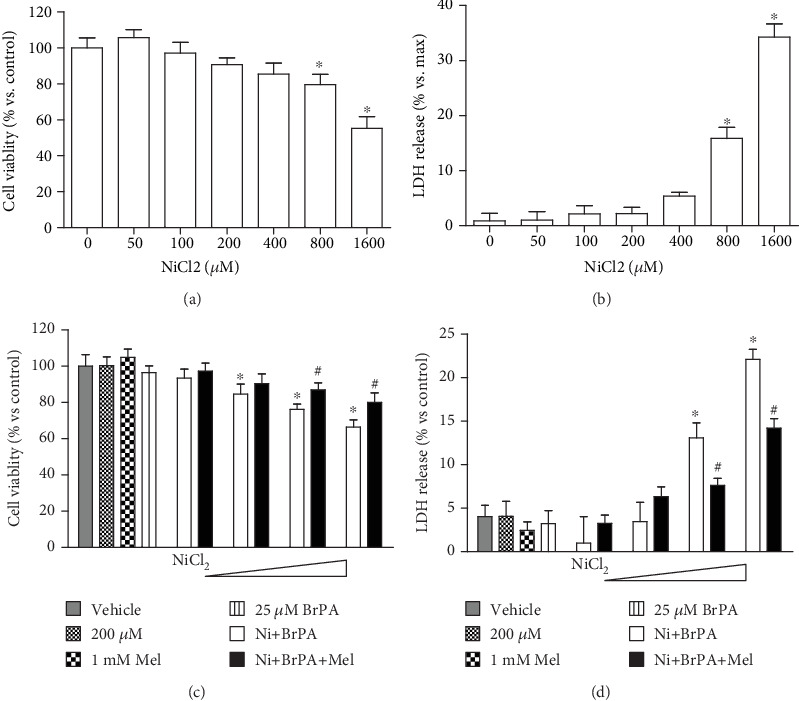
Effect of melatonin on nickel and BrPA coexposure induced cytotoxicity. Single nickel exposure induced cytotoxicity in BEAS-2B cells was measured with cell viability and LDH release experiments. Cells exposed to different concentrations of NiCl2 (50-1600 μM) for 24 h (a and b). A glycolysis inhibitor, bromopyruvic acid (BrPA), was applied to coexpose with nickel. At the approach of 18 h post NiCl2 administration, 1 mM melatonin was added and incubated with cells for an additional 6 h. The effect of melatonin on BrPA and NiCl2 cotreatment induced cell death was measured with cell viability (c) and LDH release (d). The error bar reflects the S.E.M. of at least three independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 compared with the nickel-free control group, and #P < 0.05 compared with the same nickel concentration but with the melatonin-free group.
