Figure 8.
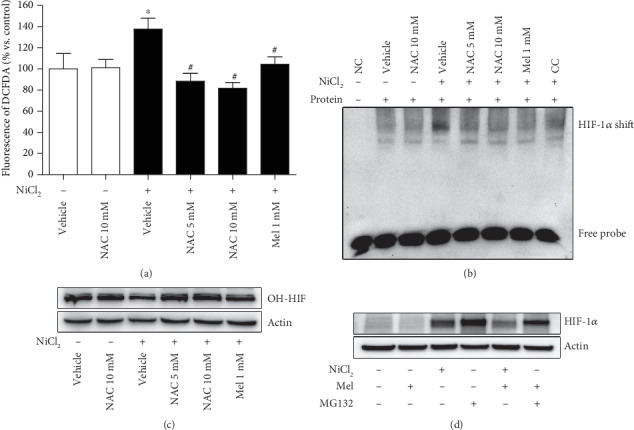
Effect of melatonin and NAC on ROS, HIF-1α transcriptional activity, and PHD activity. The effects of melatonin and NAC on nickel-increased cellular ROS level were measured using a DCFDA fluorescence probe (a). The effects of melatonin and NAC on nickel-induced DNA binding activity of HIF-1α were evaluated by EMSA assay ((b): NC—no protein control; CC—competition control). The hydroxy-HIF-1α (OH-HIF) levels which manifest the activity of prolyl hydroxylases (PHD) were evaluated in treated cells with western blot (c). MG132, a proteasomal inhibitor, also caused HIF-1α accumulation. The effects of melatonin to destabilize the HIF-1α accumulation induced by nickel or MG132 were evaluated (d). The error bar reflects the S.E.M. of at least three independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 compared with the nickel-free control group. #P < 0.05 compared with the same nickel concentration but with the melatonin- or NAC-free group.
