Fig. 1.
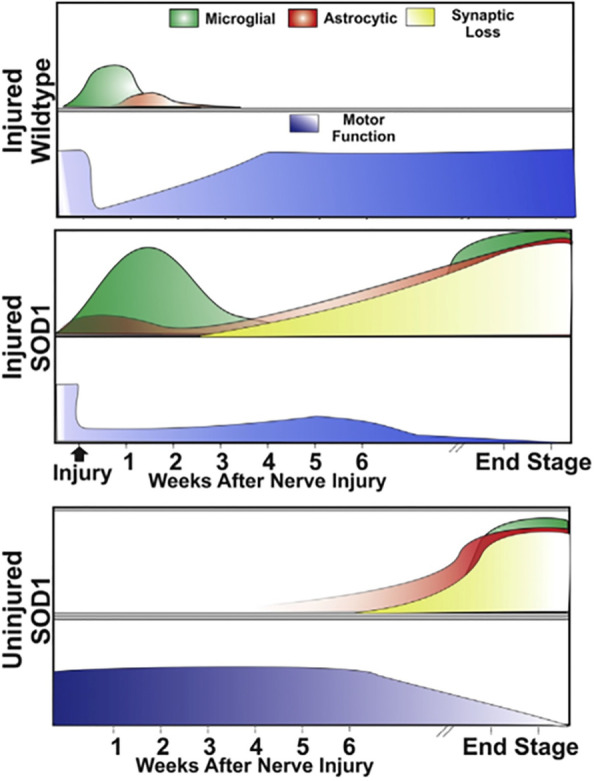
Time course of injury-induced functional, inflammatory, and neuronal changes in the SOD1 rat. This figure summarizes the longitudinal effects of mutant SOD1 protein both on motor function and cellular pathophysiology after a single sciatic nerve injury. While WT animals recovered fully from the injury within 5 weeks, they had only mild microgliosis/astrocytosis in the acute recovery stage. In contrast, injured SOD1 animals failed to recover and showed increased and sustained microgliosis followed by a premature astrocytic recruitment and neuronal synaptic loss. This model combines an environmental insult with a genetic defect that can help elucidate the functional and physiological effects of ALS disease onset and progression that could be used to develop targeted therapeutics (taken from [18] with the permission)
