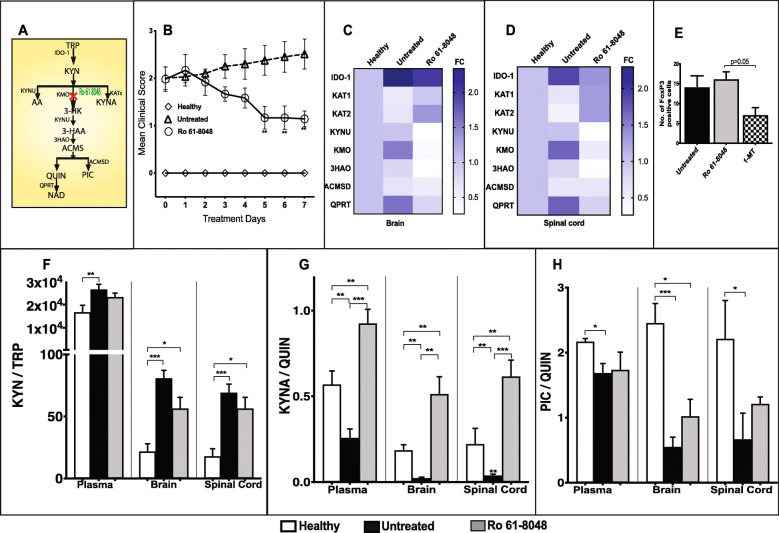
Fig. 6.
Delayed modulation of KP reverses the progression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). a Schematic illustration of kynurenine pathway (KP). b Mean EAE clinical scores of healthy control (◊, n = 6), untreated EAE control (Δ, n = 6), and Ro 61-8048 treated EAE mice (KMO inhibitor; O; n = 6), 100 mg/kg; i.p. daily for 7 days (mean ± SD, *p < 0.05 (Ro 618048 vs untreated EAE)). c and d The heat maps show KP gene expression in the brain (c) and spinal cord (d) of healthy, untreated and Ro 61 8048 treated EAE mice. Gene expression ranges from high (dark blue) to low (white). e FoxP3 (forkhead box protein) expression was measured in spleen of 1-MT and Ro 61-8048 treated EAE-induced mice (EAE score 2). f–h Changes in KP metabolites upon treatment with Ro 61-8048. The line diagrams depict kynurenine and tryptophan (KYN/TRP) ratio (f), kynurenic acid, and quinolinic acid (KYNA/QUIN) ratio (g), and picolinic acid and quinolinic acid (PIC/QUIN) ratio (h) measured (mean ± SD) in the plasma, brain, and spinal cord of healthy (white; n = 8), untreated EAE (black; n = 6), and Ro 61-8048 (gray; n = 3) treated mice. Three symbols: p ≤ 0.001; two: p ≤ 0.01; one: p ≤ 0.05. IDO-1, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; KAT, kynurenine amino transferase; KYNU, kynureninase; KMO, kynurenine monooxygenase; 3HAO, 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase; ACMSD, 2-amino-3-carboxymuconatesemialdehyde decarboxylase; QPRT, quinolinate phosphoribosyl transferase