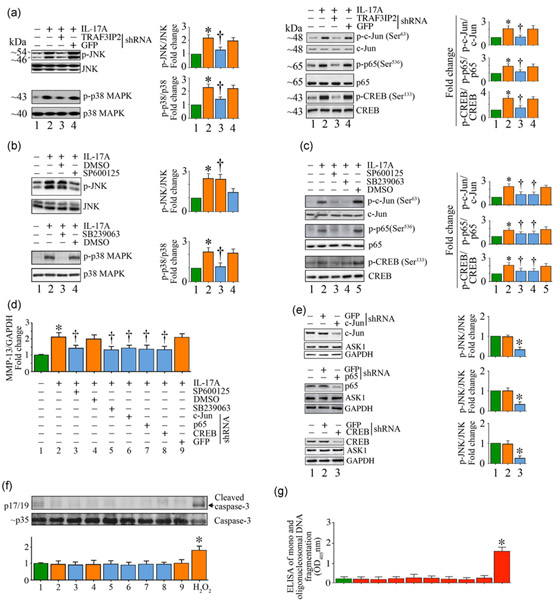
FIGURE 3.
IL-17A induces MMP-13 expression via JNK, p38 MAPK, AP-1, NF-κB, and CREB. (a) IL-17A induces JNK, p38 MAPK, AP-1, NF-κB, and CREB activation via TRAF3IP2 as measured by immunoblotting using activation-specific antibodies. (b) IL-17A-induced JNK and p38 MAPK activation was inhibited by SP600125 and SB239063, respectively. (c) Targeting JNK and p38 MAPK attenuates IL-17A-induced AP-1 (c-Jun), NF-κB (p65), and CREB activation. Quiescent SMC treated as in (b) were analyzed for AP-1, NF-κB, and CREB activation by immunoblotting using activation-specific antibodies. (d–f), Targeting JNK, p38 MAPK, AP-1, NF-κB, and CREB suppresses IL-17A-induced MMP-13 induction, without affecting cell viability. JNK and p38 MAPK were targeted by pharmacological inhibitors as in (b), and AP-1, NF-κB, and CREB were targeted by lentiviral shRNA. MMP-13 mRNA expression was measured by RT-qPCR (d), and knockdown of AP-1, NF-κB, and CREB was confirmed by immunoblotting (e). Cell death was analyzed by caspase-3 activation by immunoblotting (f) and quantification of mono- and oligonucleosomal fragmented DNA in cytoplasmic extracts by ELISA (g). (a–c,e,f) The intensity of immunoreactive bands from three independent experiments is semiquantified and summarized in the respective right-hand side or bottom panels. The results are expressed as mean ±SE. DMSO: dimethyl sulfoxide; ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; GFP: green fluorescent protein; IL: interleukin; MMP-13: matrix metalloproteinase-13; OD: optical density; RT-qPCR: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; shRNA: short-hairpin RNA; TRAF3IP2: TRAF3 Interacting Protein 2. *p < at least 0.01 versus untreated; †p < at least 0.01 versus IL-17A