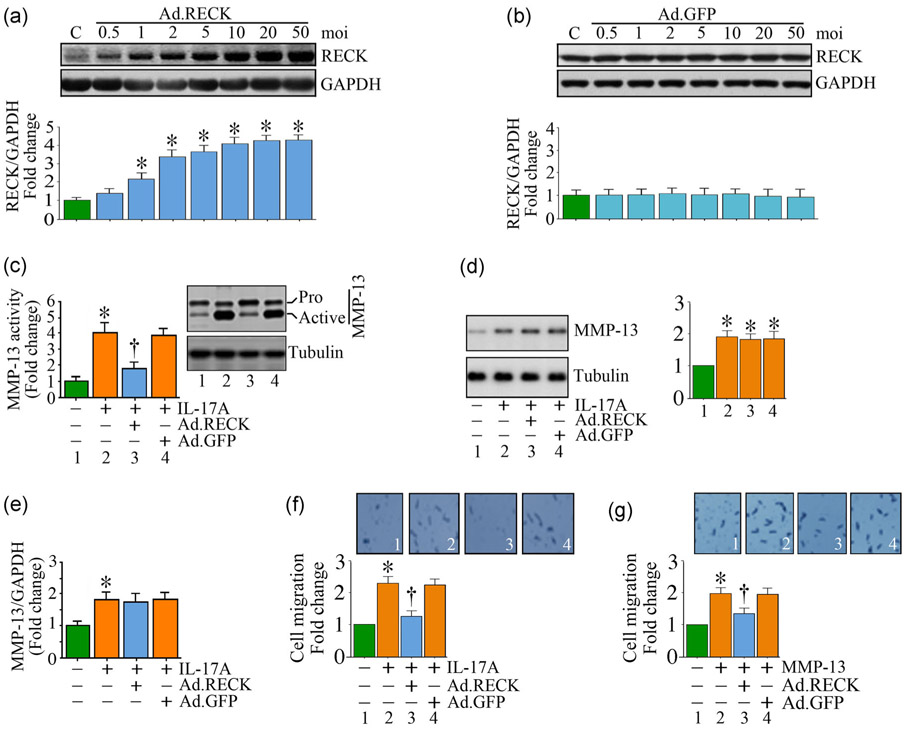
FIGURE 7.
RECK overexpression blunts IL-17A- and rMMP-13-induced SMC migration. (a,b) Adenoviral transduction of RECK (Ad.RECK; a), but not control GFP (Ad.GFP; b), increases RECK expression in a dose-dependent manner. (c-e) Ectopic expression of RECK by adenoviral transduction (moi 10) inhibits IL-17A-induced MMP-13 activity (c), but not its total protein (immunoblotting; d) or mRNA expression (RT-qPCR; e). (f,g) Ectopic expression of RECK inhibits IL-17A- (f) and rMMP-13 (g)-induced SMC migration. (f,g) Insets show images of cells migrated to the other side of the Matrigel™ basement membrane. (a,b,d) The intensity of immunoreactive bands from three independent experiments is semiquantified by densitometry and summarized in the bottom or right-hand side panels. GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GFP: green fluorescent protein; IL: interleukin; MMP-13: matrix metalloproteinase-13; mRNA: messenger RNA; RECK: reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with kazal motifs; RT-qPCR: quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; SMC: smooth muscle cell. *p < at least 0.01 versus untreated; †p < at least 0.01 versus IL-17A