Figure 4.
RBD-Specific Antibody Titers as a Surrogate of Neutralization Potency in Acutely Infected COVID-19 Patients
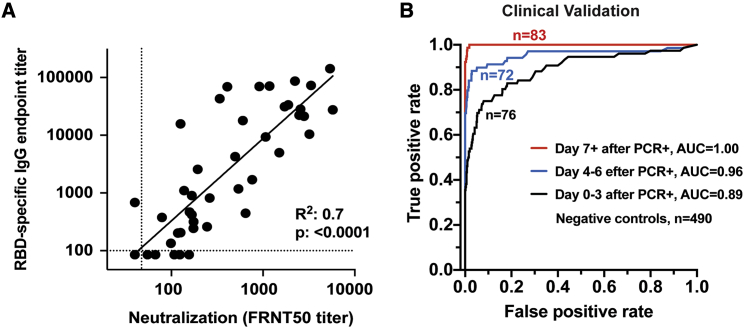
(A) Comparison of RBD-specific IgG endpoint titers with SARS-CoV-2-specific FRNT50 titers. Correlation analysis was performed by log transformation of the endpoint ELISA or FRNT50 titers followed by linear regression analysis.
(B) The RBD-specific ELISA was validated for high-throughput clinical testing in Emory Medical Laboratories. Sera (n = 231) were collected from COVID-19 patients within the first 22 days after PCR-confirmation (Table S1). Sera (n = 490) collected in 2019 were used as negative controls. ROC curves are shown comparing the true-positive and false-negative rates of the ELISA using different OD cutoffs and sera collected at different times post-infection. Whereas the RBD ELISA produced an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.89 when samples were collected close to the time of infection (within 3 days of positive PCR; n = 76), longer sampling times resulted in better performance. Assay performance was nearly perfectly discriminatory (AUC = 1.00) when samples were collected at least 7 days after the positive PCR (n = 83).