Abstract
Purpose
Recognition of disparities for vulnerable populations in the field of oncology is increasing, but little attention has been paid to deaf patients. At least a million Americans are culturally deaf and use American Sign Language. Poor linguistic and cultural competency among physicians is a barrier to care delivery for these patients, placing them at risk for treatment disparities. To better educate oncology practitioners, including radiation oncologists, regarding the unique needs of this cohort, we performed an evidence-based literature review of culturally competent care for deaf patients to improve patient care and delivery.
Methods and Materials
PubMed was systematically reviewed for publications reporting on deaf patients for articles regarding (1) survivorship, patterns of failure, or toxicity in treating malignancies or (2) cultural and linguistic barriers to delivery of oncological care. Publications were excluded if deafness was a side effect of treatment or barriers and outcomes were reported on nonmalignant conditions.
Results
Barriers to care were poor health literacy, accessibility to providers or resources in preferred language (ie, American Sign Language), and limited cultural and linguistic proficiency of providers. Deaf patients may have a delay in cancer diagnosis, but no articles reported on treatment outcomes for malignancies in deaf patients. Currently, no oncology-specific guidelines exist on care delivery for deaf patients with cancer. We propose the need for a care model that provides guidelines on creating effective and total communication accessibility for deaf patients and improves cultural and linguistic competency among providers. Guidance should be provided on implementation of resources and training for oncology practitioners and how their respective institutions and staff can help create inclusive care environments.
Conclusions
Clinical outcomes of deaf patients with cancer remain poorly characterized, highlighting the need for a care model to promote provision of linguistically and culturally competent oncological care for deaf patients.
Introduction
Although recognition of disparities in outcomes for many vulnerable populations in the field of oncology is increasing, little attention has been paid to the outcomes of deaf patients with cancer. Of the subset of Americans who have at least moderately to severely profound hearing loss, at least a million of these Americans identify as culturally deaf and use American Sign Language (ASL),1 which may be an underestimate given the difficulty of performing an accurate census of this group. ASL users and culturally deaf people have unique linguistic and cultural needs that distinguish them from others with hearing loss as a result of aging, traumatic damage to the hearing apparatus at an advanced age, and those who develop hearing loss as a result of medical treatment. Moreover, within this group, one finds a diverse amalgam of immutable factors including peoples of multiple races, ethnicities, ages, and a wide continuum of demographic characteristics such as language preferences, education, socioeconomic status, and health literacy. There have been an increasing number of public health initiatives among hospitals and medical education programs in recent years2, 3, 4 to educate and increase awareness among physicians and other health care providers. Despite that, the vast majority of physicians have very limited training that teaches them how to deliver health care to these patients at a linguistically and culturally competent level.
The minimum requirement was defined in 1990 by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), which states health care systems and providers are required to ensure effective communication with patients through reasonable accommodations.5 The term effective communication can be very vague and does not clearly delineate the needs to someone not well versed with this group. This is highlighted by the fact that there have been multiple studies identifying poor linguistic and cultural competency among physicians as a significant barrier to care delivery for these patients, placing them at risk for treatment-related disparities. For example, Iezzoni et al6 performed focused group interviews on the experience of deaf adults with the general health care system and found that physicians frequently required them to use inadequate modes of communication, did not understand their responsibility to ensure effective communication, and often complained about the difficulties of hiring interpreters or providing special equipment. Another study on deaf women in the United Kingdom found that fewer than 1 in 10 deaf women said they fully understood what their physician said to them when they came in for a clinic visit on their own.7 To better educate oncology practitioners, including radiation oncologists (ROs), regarding the unique needs of this cohort in the oncology setting, we performed an evidence-based literature review of culturally competent care for deaf patients with the goal of identifying potential barriers to care and providing some considerations for a future care model to improve care and delivery for deaf patients.
Methods and Materials
Literature review
A systemic literature search was conducted using PubMed for publications with the search terms “Deaf AND Cancer.” Then, “Deaf” was interchanged with keywords such as “Hard of Hearing,” “Hearing Loss,” “Hearing Impaired,” “ASL,” and “Deaf Culture.” The following filters were applied: publications after 1990; English; and human species. Studies were then screened by title and abstract to determine eligible articles for review. Articles were included for analysis if they reported on deaf patients with a malignancy; their knowledge, experiences, or perspectives in regards to cancer; survivorship, patterns of failure, and toxicity with various treatment modalities for these patients; or cultural or linguistic barriers to delivery of optimal oncological care. Publications were excluded if they reported on deafness or hearing loss as a side effect of treatment, or if they reported on outcomes or barriers in deaf patients with nonmalignant conditions. Eligible articles were then reviewed in entirety with an emphasis on identifying treatment outcomes or barriers to care for the patient cohort of interest. The references for selected articles were also reviewed for additional articles not identified using the search terms but that met inclusion criteria. To maintain a broad scope but to also limit the search to publications with data more relevant to the modern era, we did not include publications before 1990.
Literature analysis and data extraction
For the qualified studies, the articles were categorized by the methodology and purpose of the study. For each study reporting on barriers in health care for deaf patients, descriptive information was collected on the type of barriers or disparities identified in the study and at what level these barriers or disparities existed in the current health care system. Because reported barriers to care across different articles were often multifaceted views of a similar theme, unifying themes were created to account for the heterogeneity of patient groups, methodology, intent of the study, and malignancies of interest. To ensure such themes were relevant to this patient population as a whole, themes were created if relevant theme-related barriers were not limited to gender or type of malignancy and if supporting data could be identified in at least 5 different studies. If a study reported on oncology treatment outcomes for deaf patients, qualitative and quantitative variables were collected including, but not limited to, age, sex, race, cancer histology, type of treatment, treatment outcomes (including local failure, distant failure, overall survival, and treatment toxicity), and length of follow-up time.
Results
Descriptive characteristics
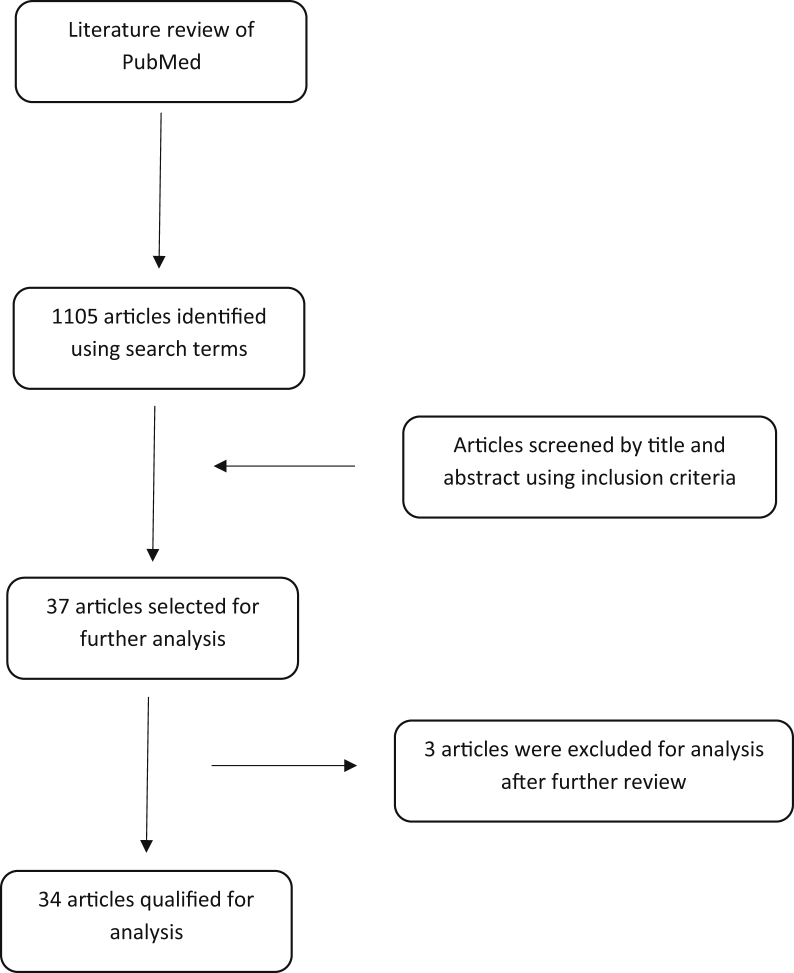
The literature search yielded 1105 potential articles, which were then screened by title and abstract. After the initial screening, 37 articles were subjected to further review with 3 being ultimately excluded for analysis in this study, leaving 34 articles3, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38 that were qualified for analysis and inclusion in this study. Of the excluded articles, 1 reported on the validation and evaluation of an online module for cancer genetics for deaf adults; another reported on the utilization of deaf-friendly ministries to promote general, including cancer-related health care information; and a third reported an educational initiative by a cancer center for medical students but did not have an oncological focus (Fig 1). Qualified studies were categorized by methodology and health care barriers/disparities are summarized in Table 1. Multiple studies (16) conducted survey-based assessments or focus group interviews of deaf patients with or without a control cohort to identify disparities in health care and overall knowledge of cancer and specific types with the majority focusing on the attitudes, practices, and perceptions of deaf adults regarding screening guidelines for certain cancers. Of note, in 1 of these 16 studies, the study cohort was composed of ASL interpreters working in the health care system instead of deaf adults.8 One study was a multi-institutional retrospective review of the diagnostic stages of deaf adults at time of diagnosis.9 Another study conducted a review of major research databases for literature on the quality and outcomes of health initiatives tailored to improving the knowledge of deaf adults while adhering to national guidelines on cancer treatment and prevention.10 The rest, 16 in total, were interventional studies designed to assess various educational initiatives in the form of programs, videos, or online modules, and so forth, which were tailored to be accessible to deaf participants. Four interventional studies were randomized, and 4 did not have any control arms.
Figure 1.
Flowchart: Systematic review of eligible articles from the PubMed database.
Table 1.
Summary series of qualified studies
| Authors | Cancer | Methodology | Study description | Health care barriers or disparities for deaf adults |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cumberland et al11 | Breast cancer | Randomized, interventional control trial | Assessment of whether participating in a culturally and linguistically tailored educational program improved the knowledge of deaf breast cancer patients with limited education | Desire to participate in regular mammography screenings increased in the interventional group and knowledge increased from baseline in the interventional group, demonstrating the benefit of accessible programs |
| Hickey et al12 | Breast cancer | Interventional study without a control cohort | Deaf women with a preference for ASL were exposed to a breast cancer education video in ASL | Disparities in knowledge about breast cancer were identified and deaf women demonstrated improved knowledge about breast cancer after utilization of an accessible resource |
| Berman et al22 | Breast cancer | Focus group interviews and survey-based assessments | Deaf breast cancer survivors were interviewed in the first and surveyed in the second study | Women expressed that their physicians did not understand how to interact or did not want to interact with them because of their deafness; inadequate communication methods were used, and there were profound health literacy disparities (some women did not even know what procedures/medications they received) |
| Berman et al23 | Breast cancer | Survey-based assessment | Survey of knowledge and health practices among deaf women with breast cancer | Disparities in knowledge about breast cancer were identified and deaf women demonstrated low compliance rates with screening guidelines for breast cancer |
| Sadler et al26 | Breast cancer | Survey-based assessments | Pilot study of deaf women surveyed about breast cancer after participating in an intervention study | Similar findings to Berman et al, Cumberland et al, and Hickey et al |
| Steinberg et al24 | Breast/ gynecologic cancers | Focus group interviews | Deaf women were interviewed regarding health literacy, knowledge of health issues, accessibility issues, and general understanding of health issues | Many women did not understand the value of cancer screening, including mammograms or pap smears and recommended medical/surgical treatments and many reported negative experiences with the health care system due to a lack of a common language with providers that did not use interpreters or demonstrate a willingness to improve communication |
| Wollin et al28 | Breast/ gynecologic cancers | Focus group interviews | 13 Australian deaf women were interviewed on their experiences with getting mammograms/pap smears | Disparities were identified in baseline knowledge about screening tests, compliance with recommended guidelines, and some perceived difficulties navigating the health care system |
| Shabaik et al13 | Gastrointestinal: colorectal cancer | Interventional study | Deaf adults watched an accessible video in ASL about CRC | Deaf adults who watched the ASL video improved their CRC knowledge, and data also supported sustained retention in the crossover cohort |
| Farber et al3 | General oncology | Interventional study without a control cohort | Medical students participated in a deaf culture education and ASL immersion program with an oncological focus | Medical students demonstrated improvements in ASL proficiency, deaf cultural competency, and were more competent in medical interactions with deaf patients. Deaf patients qualitatively reported overwhelming positive experiences with participants in the program |
| Palmer et al4 | General oncology | Parallel, 2:1 randomized prepost interventional study | Does the provision of bilingual educational modalities improve knowledge of cancer genetics compared with monolingual modalities? | Bilingual modalities improved the cancer genetic knowledge of patients with low education, and these patients were more likely to see a genetic counselor or have cancer genetic testing based on a physician’s recommendation |
| Zazove et al7 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment | Deaf adults took a reading comprehension test | Higher scores were associated with greater comfort in discussing cancer with physicians and lower scores were associated with ASL use with providers and deaf community membership, suggesting that adults preferentially using ASL with limited access to English proficiency may be experiencing disparities in understanding and acquiring relevant health care information |
| Hommes et al8 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment of ASL interpreters | Investigational study on the perception of interpreters on barriers for effective communication for deaf patients in health care | Health care providers were perceived as not understanding how to adequately meet communication needs for deaf patients with limited understanding by deaf patients of their diagnosis; overreliance on video-based interpreting and lack of empowerment among deaf patients to advocate for their preferences |
| Druel et al9 | General oncology | Multi-institutional chart review | Deaf patients with cancer treated in 5 French hospitals were identified and their diagnostic stages were compared with hearing peers | Deaf patients may present with more advanced stages of prostate, melanoma, and colorectal cancer than hearing peers, raising concern for limitations in access to public health campaigns and screening programs |
| NaseriBooriAbadi et al10 | General oncology | Systematic literature review | Research databases were searched for articles on educational programs with the aim of improving knowledge and attitudes of deaf patients toward cancer | Health literacy of deaf patients is poor, and educational interventions tailored for deaf people have shown the ability to improve literacy in this cohort |
| Berman et al14 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment | Faculty at 4 schools for the deaf were surveyed regarding tobacco use in young deaf adults | Limitation of accessible curriculum and materials were barriers to educate young deaf adults on healthy practices and attitudes on tobacco use |
| Orsi et al25 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment | Deaf adults were surveyed on knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors toward cancer screening tests and compliance rates | Females who reported using an interpreter primarily to communicate with their physician were more likely to have a pap smear compared with their deaf peers and only 48% of females could correctly identify a pap smear. Despite undergoing screening for various cancers, many participants could not clearly define the screening tests despite placing a high importance on screening in general. A higher than normal number of patients had access to interpreters and physicians using ASL in this study, suggesting that are there still linguistic and cultural disparities at play that remain to be fully addressed |
| Zazove et al27 | General oncology | Cross-sectional survey-based assessment | Deaf adults were given 4 ways to complete a questionnaire including knowledge of cancer prevention recommendations by way of voice, an ASL video, captions, or printed English | Lower scores occurred when participants used ASL or another language at home, wrote notes to communicate with physicians/nurses, or used an interpreter or ASL with physicians/nurses, suggesting that effective communication needs were not being met for ASL users |
| Berman et al29 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment | Deaf college students were surveyed on tobacco attitudes and practices | Although deaf adults had lower smoking rates than the general population at the time of the study, they were more likely to try smoking and also try multiple types of tobacco. Only 20% reported ever seeing an antitobacco advertisement geared toward deaf people |
| Berman et al30 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment | Deaf middle and high school students were surveyed on tobacco attitudes and practices | Smoking use was lower in deaf patients than in the average high school population and mainstreamed students were more likely to try tobacco than deaf school peers, suggesting that deaf patients undergo different health care pressures than hearing peers and that deaf patients are a heterogeneous group |
| Engelberg et al31 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment of deaf participants | Assessment of whether provision of accessible health information with ASL humor improved the health literacy and practices of participants | Participants’ health literacy improved with accessible resources, and they were more likely to retain knowledge and share with others, showing the benefit of accessible resources in this population |
| Kushalnagar et al34 | General oncology | Interventional study of deaf and hearing adults | Does simplifying health cancer text on the internet make information more accessible for deaf patient? | There may be a marginal benefit to simplifying text for deaf adults to improve accessibility to cancer-related resources |
| Tamaskar et al35 | General oncology | Survey-based assessment | Deaf and hearing adults were surveyed on their attitudes about preventive medicine including cancer prevention | Deaf people may be more likely to receive cancer screening tests than hearing peers, but it is unclear whether they understood the rationale and value of these tests |
| Zazove et al36 | General oncology | Interventional study | Deaf people watched a video on cancer with half receiving an accessible version with captions, ASL | Language utilization was not associated with improved knowledge scores, but on multivariate analysis, having a hearing spouse and a greater number of sources was associated with improved scores suggesting some patients are able to gain accessibility in more ways than others |
| Berman et al39 | General oncology | Interventional study | Four schools for the deaf were provided with an accessible curriculum for educating young deaf adults on tobacco use | Accessible programming may lead to a decrease in tobacco use and increase in knowledge of the health consequences of tobacco use and antitobacco attitudes in young deaf adults |
| Folkins et al15 | Genitourinary: testicular cancer | Interventional study without control | Deaf men watched a prostate and testicular cancer video with ASL and captions to improve their knowledge about the mentioned cancer | General perception exists among deaf men that there are limited accessible resources providing health care information but when provided deaf men were able to benefit by demonstrating increased awareness of prostate/testicular cancer |
| Sacks et al37 | Genitourinary: testicular cancer | Interventional study | Deaf and hearing men were exposed to a testicular cancer video (made accessible in ASL for deaf participants to improve the general/testicular cancer knowledge of participants) | Deaf men were at a disparity regarding baseline knowledge but demonstrated ability to improve their knowledge when exposed to an accessible educational video |
| Kaskowitz et al16 | Genitourinary: prostate cancer | Interventional study without control | Prostate cancer educational program in ASL was developed for deaf men to improve knowledge of prostate cancer and adherence to screening recommendations | Barriers listed among patients for obtaining health care information included communication with doctors (40%) and lack of resources including interpreters (26.1%), and at least 75% of patients reported at least 1 barrier. Participants’ knowledge of prostate cancer improved after participating in the study, but it was higher in the subset with ASL as the preferred mode of communication |
| Kushalnagar et al33 | Genitourinary: prostate cancer | Survey-based assessment of deaf and hearing males with prostate cancer | Public health study investigating the role of communication accessibility in SDM for prostate cancer screening | Deaf men were less likely to be engaged in SDM than hearing peers, possibly due to lack of accessible accommodations in preferred language (ie, ASL) and lack of a regular physician-patient relationship |
| Choe et al17 | Gynecologic: cervical cancer | Blinded, randomized trial | Deaf women participated in an accessible educational program about cervical cancer | Deaf patients were able to improve their cervical knowledge after watching an ASL video and were able to retain this knowledge at follow-up; they were also more likely to share or watch the video again than those who did not watch an ASL video |
| Jensen et al18 | Gynecologic: ovarian cancer | Interventional study | Deaf and hearing women were exposed to a video on ovarian cancer for the purposes of improving the general/ovarian cancer knowledge of participants | Deaf women were at a disparity regarding baseline knowledge but demonstrated ability to improve their knowledge when exposed to an accessible educational video |
| Yao et al19 | Gynecologic: cervical cancer | Interventional study | Deaf and hearing adult women were exposed to a cervical cancer education video to improve the cervical cancer knowledge of participants | Deaf women were at a disparity regarding baseline knowledge of cervical cancer but demonstrated ability to improve their knowledge when exposed to an accessible educational video |
| Wang et al21 | Gynecologic: cervical cancer | Blinded, randomized trial | Deaf women participated in an accessible educational program about cervical cancer | The internal health locus of control for deaf women did not predict for their baseline knowledge or ability to improve but women who watched the video in ASL did have improved knowledge scores over time suggesting that accessibility was more important than self-directed behavior in improving outcomes |
| Spellun et al32 | Gynecologic: cervical cancer | Survey-based assessment | Deaf and hearing adult males and females 18-26 years old were asked questions using a survey about HPV and cervical cancer | Hearing participants were more likely to know that HPV can cause cervical cancer and that there is an HPV vaccine, identifying a disparity in health literacy and limited access to accessible informational health care resources |
| Kushalngar et al38 | Lung cancer | Survey-based assessment | Deaf adults were surveyed about patient- centered communication, modes of communication, smoking status, and lung cancer screening in ASL | Deaf adults were more likely to be ask about a lung cancer screening test when they were provided with accessible options, such as an ASL interpreter |
| Harry et al20 | Skin cancer | Interventional study | Deaf adults were exposed to a skin cancer education video to improve the skin cancer knowledge of participants | Deaf patients were able to improve their skin cancer knowledge after watching an ASL video and were able to retain this knowledge at follow-up |
Abbreviations: ASL = American Sign Language; CRC = colorectal cancer; HPV = human papillomavirus; SDM = shared decision making.
Health care barriers
Multiple health care barriers were identified at several different levels in the health care system, but 3 unifying themes were present: (1) poor health literacy among deaf adults; (2) accessibility to tailored health care resources for cancer-specific information; and (3) poor linguistic and cultural competency among physicians (Table 2). In every study, a common denominator was poor health literacy of deaf youth or adults at baseline compared with average expected literacy levels for hearing peers. For example, multiple interventional studies in our series conducted preintervention surveys and found that deaf adults consistently had statistically significant lower baseline scores for cancer-specific knowledge and were more likely to not understand the value of or recognize cancer-specific screening tests.4,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21 In the most extreme example, a focus group interview study reported that a breast cancer survivor stated she did not know what cancer was when asked, despite being a survivor.21 However, other variables, beyond deafness, may also be in play such as socioeconomic status, level of education, language preference, and so forth. Palmer et al4 reported that level of education was associated with participants’ baseline level of knowledge and ability to improve postintervention. Another study identified the level of reading comprehension to be significantly associated with the level of comfort deaf patients had discussing cancer with their physicians.7
Table 2.
Barriers to effective utilization of the health care system for deaf patients with cancer
| Poor health literacy among deaf patients | Baseline health literacy and cancer-specific knowledge for deaf youth or adults was lower than average expected levels for hearing peers |
| Availability of tailored health care resources for cancer-specific information | Lack of educational resources, programs, and initiatives that are linguistically and culturally accessible |
| Poor linguistic and cultural competency among physicians | Limited training, experience, and bias prevents physicians from providing effective communication and practicing in a culturally sensitive manner |
A second barrier to care is poor health literacy or differences in cancer-specific attitudes and practices. However, this may be reflective of the limited amount of health care resources that are accessible and tailored to this population rather than the fact that patients are deaf. Multiple studies in our series reported on interventional programs designed to improve cancer-specific knowledge in deaf participants and overwhelmingly showed that the knowledge of deaf patients about specific cancers improved after they had access to an accessible resource on the topic. Moreover, those same studies showed that accessible programs can lead to better adherence to cancer-specific screening recommendations or avoidance of carcinogens such as tobacco use in deaf youth.4,11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21 The third barrier was deaf patients’ frustration with the health care system and the lack of linguistically and culturally competent health care providers. A survey of ASL interpreters showed that multiple providers did not understand what effective communication with deaf patients entailed and thought inferior methods such as lip-reading were acceptable forms of communication.8 Berman et al22 reported that several women stated that their doctors did not understand their deafness and failed to communicate with them about their cancer. Multiple studies showed that preference for ASL or ASL utilization at home or with health care providers was associated with detrimental experiences or outcomes, highlighting the poor level of linguistic competency among practitioners in general.7,8,22, 23, 24, 25, 26 Kaskowitz et al16 surveyed deaf patients in a prostate cancer education program and almost half reported that communication with physicians was a barrier to obtaining health care information. Another study investigated baseline knowledge of cancer prevention recommendations in deaf adults, and found that lower scores were associated with use of ASL at home or written notes with their providers, compared with those patients who spoke English at home or with their physician.27 Several educational initiatives have been developed to address this. For example, an ASL and deaf culture and cancer program was developed for medical students at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine to teach students about deaf culture and to help them gain proficiency in ASL. Deaf patients who worked with participating students reported overwhelming positive qualitative responses, and students were better equipped to interact with deaf patients, improving health care delivery.3
Oncological treatment outcomes
A multi-institutional retrospective series of 5 French hospitals identified 80 deaf patients diagnosed with and treated for cancer from 2005 to 2014. This study found that deaf patients may present at more advanced stages at time of diagnosis for certain cancers compared with their hearing peers, such as for prostate or colorectal cancer.9 This was only a small study of 80 patients and included a review of patients in a specific geographic subset, raising the issue of generalizability of these results. Our literature search revealed that there have not been any studies reporting on whether deaf patients are at a disparity in the type of medical or surgical treatment they receive in comparison with their hearing counterparts. Data on whether deaf patients are getting treatment that adheres to national guidelines and whether their treatment outcomes are, at least, not inferior in terms of measurable variables such as survivorship or patterns of failure are not currently available in the literature.
Discussion
Our literature review identified 3 unifying health care barriers for deaf cancer patients, namely (1) poor health literacy among deaf adults; (2) accessibility to tailored health care resources for cancer-specific information; and (3) poor linguistic and cultural competency among physicians. These results are not necessarily uniformly generalizable. Deaf patients are not a homogenous group; they demonstrate remarkable geographic, racial, and socioeconomic diversity. The quality and level of communication accessibility at home can vary dramatically, with the majority of patients being shaped at a young age by birth into hearing families, most of whom having limited to no proficiency in ASL. Moreover, educational and literacy levels are also driven in large part by limiting factors outside of the health care system, which can prevent any attempts by the health care system to significantly improve the generally poor health literacy of these patients. Furthermore, there were no large-scale series in our study, and much heterogeneity in the demographics of patients participating in these studies. However, Pollard et al40 showed that well-educated people with high school or college degrees in the United States still had lower than expected health literacy. This suggests that the barriers to health care are also due to inadequacies in the health care system and its lack of accessible resources. Our review identified multiple interventional programs designed to educate deaf patients with the aim of improving the quality of accessible cancer-specific health care resources, which appear to be beneficial for deaf patients. Despite multiple studies reporting on frustration with the linguistic and cultural competency of providers, only 1 study in this series focused on addressing these deficiencies in health care practitioners, specifically medical students.3 Most physicians have not had access to similar educational initiatives about deaf culture and likely have limited to no training or knowledge of ASL. There are legal recommendations in the form of laws such as the ADA and national organizational guidelines to guide the provision of accessible healthcare delivery such as those from the National Association of the Deaf (NAD), but the significance of these resources are limited in practice.41 Again, the wording of the ADA regarding deaf patients is ambiguous and does not provide physicians with a clear definition of what is entailed in “effective” communication with a deaf patient. The National Association of the Deaf guidelines are very informative, but largely underused as they are a small body with a message that does not reach most physicians. Physicians are without any oncology-specific resource to guide them on how to optimize care delivery to deaf patients and compensate for their limited training and exposure to this population. We propose the need for a care model that provides guidelines on creating effective and total communication accessibility for deaf patients, and addresses the cultural and linguistic heterogeneity within this cohort, taking into account factors that can influence the physician-patient relationship including familial, cultural, health literacy, and socioeconomic dynamics.
Disparate outcomes experienced by deaf patients in other health care settings have also been documented in the literature. Physicians in the United States were surveyed and reported deaf patients were more likely than hearing patients to have greater difficulty in communicating with them, trusted them less, and were less likely to understand their diagnosis and treatment.42 Similar findings were documented in a large study by an organization in the United Kingdom, SignHealth.43 In New Zealand, 40% of deaf patients do not feel there is adequate accessibility to interpreters in health care, and this was associated with a worse quality of life.44 In the primary care setting, dedicated efforts have been made to develop care models for improving health care delivery to the deaf population. In Austria, a comprehensive program was developed that provides health centers for the deaf attached to general hospitals that are staffed by culturally and linguistically competent providers. This has become the de facto primary care facility for many deaf Austrians.45 In France, dedicated outpatient primary care facilities have been beneficial for the deaf community.46 Such examples serve to highlight the potential benefit of an oncological care model for the deaf-physician patient relationship.
Considerations for a future RO care model
We envision the care model would allow physicians to create inclusive health environments by providing total communication accessibility within culturally appropriate framework. It would serve as a resource to navigate the cultural and linguistic nuances of interacting with deaf patients. This should be based on a robust understanding of the deaf identity, where deaf patients view themselves as more than just a disability group, but rather a linguistic and cultural minority. Physicians should be guided on the provision of individualized care, accounting for the fact that deaf patients are a very diverse group of people, a smorgasbord of racial and ethnic identities; can have multiple linguistic and cultural associations in addition to ASL and the deaf culture; and run the spectrum of socioeconomic status and educational backgrounds. It would clearly delineate what entails effective communication in the health care setting, clearly defining the ideal communication modalities, and how to provide this at various levels of the health care system. Significant weight should be given to how to develop optimal accessibility for varying services and resources in ASL, along with what entails effective procurement and utilization of qualified ASL interpreters. Opportunities to gain further exposure or the development of educational initiatives that allow physicians to gain cultural competency or ASL proficiency while in practice or training should be discussed. As this issue has remained largely unaddressed, oncology practitioners including ROs should set the standard for providing culturally sensitive and linguistically competent oncological care for deaf patients, and these guidelines should be made applicable to physicians and providers in the other fields of oncology, such as medical or surgical oncology. While in anticipation of such guidelines, physicians should focus their efforts on taking concrete steps to create total communication accessibility for their patients. This can be done by creating accessibility to ASL interpretation for all clinical encounters. ASL interpreters should be chosen based on their mastery of the language, cultural understanding, and adherence to ethics, and should have demonstrated competence with national or state interpreting certifications. Although in-person interpreting is preferred for such encounters, if that is not possible, physicians should consider providing alternatives such as video remote interpretation. Practices located in a large metropolitan area may have proximity to a large deaf community, representing a great opportunity to engage that community for advice on how to improve quality of interpretation and general guidelines about accessibility. Hospitals often have a patient and family advisory council, which members of the community can participate in to provide such community advice for a hospital. If a robust community is not present in the hospital location, then simply asking a deaf patient about his or her opinion about language/communication accessibility is important in providing quality care.
Limitations of this study include those inherent to a retrospective literature review. Most of our studies contained a small cohort of patients, and the characteristics of the patients varied widely across series, making it difficult to control for other cofounding variables that could have influenced outcomes. The majority of the studies had a narrow focus geared toward developing and implementing educational initiatives for preventive care or reporting on qualitative experiential outcomes, which can be very subjective and easily influenced by bias. Only 1 study attempted to collect quantitative data on current clinical or treatment outcomes for deaf cancer patients,9 limiting our ability to make meaningful large-scale analyses of oncological outcomes in this cohort.
We hope this review will lead to an increased emphasis among physicians in providing linguistically and culturally competent oncological care to deaf patients and a charge for the implementation of oncology-specific guidelines on specialty, regional, and national levels. Increasing awareness among physicians and creating acceptable standards should lead to improved health care delivery as has been noted for other diverse groups. Furthermore, there is a lack of literature on the treatment outcomes of deaf patients with cancer and whether disparities exist on rates of and adherence to national cancer-specific guidelines are not known. Future research should examine whether these patients have equivalent treatment outcomes, because data on patterns of failure and survivorship are not reported in this population in regards to treatment with different modalities, including radiation.
Conclusions
The clinical outcomes of deaf patients with cancer remain poorly characterized, highlighting the need for a care model for oncology practitioners to guide the provision of linguistically and culturally competent oncological care for deaf patients.
Footnotes
Sources of support: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Disclosures: none.
References
- 1.Steinberg A.G., Barnett S., Meador H.E., Wiggins E.A., Zazove P. Health care system accessibility. Experiences and perceptions of deaf people. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21:260–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1497.2006.00340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berman B.A., Guthmann D.S., Crespi C.M., Liu W. Development and testing of an antitobacco school-based curriculum for deaf and hard of hearing youth. Am Ann Deaf. 2011;155:592–604. doi: 10.1353/aad.2011.0009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Farber J.H., Nakaji M.C., Sadler G.R. Medical students, deaf patients and cancer. Med Educ. 2004;38:1201. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.02010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Palmer C.G., Boudreault P., Berman B.A. Bilingual approach to online cancer genetics education for deaf American Sign Language users produces greater knowledge and confidence than English text only: A randomized study. Disabil Health J. 2017;10:23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2016.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Americans With Disabilities Act of 1990, Pub. L. No. 101-336, 104 Stat. 328(1990).
- 6.Iezzoni L.I., O'Day B.L., Killeen M., Harker H. Communicating about health care: Observations from persons who are deaf or hard of hearing. Ann Intern Med. 2004;140:356–362. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-140-5-200403020-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zazove P., Niemann L.C., Gorenflo D.W. The health status and health care utilization of deaf and hard-of-hearing persons. Arch Fam Med. 1993;2:745–752. doi: 10.1001/archfami.2.7.745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hommes R.E., Borash A.I., Hartwig K., DeGracia D. American Sign Language interpreters perceptions of barriers to healthcare communication in deaf and hard of hearing patients. J Commun Health. 2018;43:956–961. doi: 10.1007/s10900-018-0511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Druel V., Hayet H., Esman L., Clavel M., Rougé Bugat M.E. Assessment of cancers' diagnostic stage in a deaf community - survey about 4363 deaf patients recorded in French units. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:93. doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3972-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.NaseriBooriAbadi T., Sadoughi F., Sheikhtaheri A. Improving cancer literacy for the deaf using deaf-tailored educational interventions: A review of the literature. J Cancer Educ. 2018;33:737–748. doi: 10.1007/s13187-017-1216-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cumberland W.G., Berman B.A., Zazove P. A breast cancer education program for d/deaf women. Am Ann Deaf. 2018;163:90–115. doi: 10.1353/aad.2018.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hickey S., Merz E.L., Malcarne V.L., Gunsauls D.C., Huang J., Sadler G.R. Breast cancer education for the deaf community in American Sign Language. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2013;40:E86–E91. doi: 10.1188/13.ONF.E86-E91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shabaik S., LaHousse S.F., Branz P., Gandhi V., Khan A.M., Sadler G.R. Colorectal cancer video for the deaf community: A randomized control trial. J Cancer Educ. 2010;25:518–523. doi: 10.1007/s13187-010-0113-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Berman B.A., Guthmann D.S., Liu W., Streja L. Tobacco prevention education in schools for the deaf: The faculty perspective. J Drug Educ. 2011;41:135–159. doi: 10.2190/DE.41.2.b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Folkins A., Sadler G.R., Ko C., Branz P., Marsh S., Bovee M. Improving the deaf community's access to prostate and testicular cancer information: Survey study. BMC Public Health. 2005;5:63. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-5-63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kaskowitz S.R., 3rd, Nakaji M.C., Clark K.L., Gunsauls D.C., Sadler G.R. Bringing prostate cancer education to deaf men. Cancer Detect Prev. 2006;30:439–448. doi: 10.1016/j.cdp.2006.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Choe S., Lim R.S., Clark K., Wang R., Branz P., Sadler G.R. The impact of cervical cancer education for deaf women using a video educational tool employing American sign language, open captioning, and graphics. J Cancer Educ. 2009;24:10–15. doi: 10.1080/08858190802665245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jensen L.G., Nakaji M., Harry K.M., Gallegos N., Malcarne V.L., Sadler G.R. Ovarian cancer: Deaf and hearing women's knowledge before and after an educational video. J Cancer Educ. 2013;28:647–655. doi: 10.1007/s13187-013-0529-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yao C.S., Merz E.L., Nakaji M., Harry K.M., Malcarne V.L., Sadler G.R. Cervical cancer control: Deaf and hearing women's response to an educational video. J Cancer Educ. 2012;27:62–66. doi: 10.1007/s13187-011-0264-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harry K.M., Malcarne V.L., Branz P., Fager M., Garcia B.D., Sadler G.R. Evaluating a skin cancer education program for the deaf community. J Cancer Educ. 2012;27:501–506. doi: 10.1007/s13187-012-0367-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang R., Aldridge A.A., Malcarne V.L., Choe S., Branz P., Sadler G.R. Health locus of control and assimilation of cervical cancer information in deaf women. J Cancer Educ. 2010;25:354–359. doi: 10.1007/s13187-010-0053-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Berman B.A., Jo A.M., Cumberland W.G. D/deaf breast cancer survivors: Their experiences and knowledge. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2017;28:1165–1190. doi: 10.1353/hpu.2017.0104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Berman B.A., Jo A., Cumberland W.G. Breast cancer knowledge and practices among D/deaf women. Disabil Health J. 2013;6:303–316. doi: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2013.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Steinberg A.G., Wiggins E.A., Barmada C.H., Sullivan V.J. Deaf women: Experiences and perceptions of healthcare system access. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2002;11:729–741. doi: 10.1089/15409990260363689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Orsi J.M., Margellos-Anast H., Perlman T.S., Giloth B.E., Whitman S. Cancer screening knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors among culturally deaf adults: Implications for informed decision making. Cancer Detect Prev. 2007;31:474–479. doi: 10.1016/j.cdp.2007.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sadler G.R., Gunsauls D.C., Huang J. Bringing breast cancer education to deaf women. J Cancer Educ. 2001;16:225–228. doi: 10.1080/08858190109528778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zazove P., Meador H.E., Reed B.D., Sen A., Gorenflo D.W. Cancer prevention knowledge of people with profound hearing loss. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24:320–326. doi: 10.1007/s11606-008-0895-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wollin J., Elder R. Mammograms and pap smears for Australian deaf women. Cancer Nurs. 2003;26:405–409. doi: 10.1097/00002820-200310000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Berman B.A., Bernaards C., Eckhardt E.A. Is tobacco use a problem among deaf college students? Am Ann Deaf. 2006;151:441–541. doi: 10.1353/aad.2006.0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Berman B.A., Streja L., Bernaards C.A. Do deaf and hard of hearing youth need antitobacco education? Am Ann Deaf. 2007;152:344–355. doi: 10.1353/aad.2007.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Engelberg M., Nakaji M.C., Harry K.M. Promotion of healthy humor cancer education messages for the deaf community. J Cancer Educ. 2019;34:323–328. doi: 10.1007/s13187-017-1305-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Spellun A.H., Moreland C.J., Kushalnagar P. Young deaf adults' knowledge of human papillomavirus and human papillomavirus vaccine's effectiveness in preventing cervical, anal, penile, and oral cancer. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:293–299. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2018.11.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kushalnagar P., Hill C., Carrizales S., Sadler G.R. Prostate-specimen antigen (PSA) screening and shared decision making among deaf and hearing male patients. J Cancer Educ. 2020;35:28–35. doi: 10.1007/s13187-018-1436-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kushalnagar P., Smith S., Hopper M., Ryan C., Rinkevich M., Kushalnagar R. Making cancer health text on the internet easier to read for deaf people who use American Sign Language. J Cancer Educ. 2018;33:134–140. doi: 10.1007/s13187-016-1059-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tamaskar P., Malia T., Stern C., Gorenflo D., Meador H., Zazove P. Preventive attitudes and beliefs of deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals. Arch Fam Med. 2000;9:518–525. doi: 10.1001/archfami.9.6.518. discussion 526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zazove P., Meador H.E., Reed B.D., Sen A., Gorenflo D.W. Effectiveness of videos improving cancer prevention knowledge in people with profound hearing loss. J Cancer Educ. 2012;27:327–337. doi: 10.1007/s13187-011-0292-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Sacks L., Nakaji M., Harry K.M., Oen M., Malcarne V.L., Sadler G.R. Testicular cancer knowledge among deaf and hearing men. J Cancer Educ. 2013;28:503–508. doi: 10.1007/s13187-013-0493-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kushalnagar P., Engelman A., Sadler G. Deaf patient-provider communication and lung cancer screening: Health Information National Trends survey in American Sign Language (HINTS-ASL) Patient Educ Couns. 2018;101:1232–1239. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2018.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Berman B.A., Guthmann D.S., Crespi C.M., Liu W. Development and testing of an antitobacco school-based curriculum for deaf and hard of hearing youth. Am Ann Deaf. 2011;155:592–604. doi: 10.1353/aad.2011.0009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pollard R.Q., Barnett S. Health-related vocabulary knowledge among deaf adults. Rehabil Psychol. 2009;54:182–185. doi: 10.1037/a0015771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.National Association of the Deaf - NAD Nad.org. https://www.nad.org/resources/health-care-and-mental-health-services/health-carehttps://www.nad.org/resources/health-care-and-mental-health-services/health-care-providers/questions-and-answers-for-health-care-providers/-providers/questions-and-answers-for-health-care-providers/ Available at: Published 2019. Accessed August 26, 2019.
- 42.Ralston E., Zazove P., Gorenflo D.W. Physicians' attitudes and beliefs about deaf patients. J Am Board Fam Pract. 1996;9:167–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sick Of It report (for professionals) Signhealth.org.uk. https://www.signhealth.org.uk/sick-of-it-report-professionals/ Available at: Published 2019. Accessed August 26, 2019.
- 44.Witko J., Boyles P., Smiler K., McKee R. Deaf New Zealand sign language users' access to healthcare. N Z Med J. 2017;130:53–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fellinger J., Holzinger D. Creating innovative clinical and service models for communication: Institut fuer Sinnes- und Sprachneurologie. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 2014;35:148–153. doi: 10.1097/DBP.0000000000000019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Amoros T., Bonnefond H., Martinez C., Charles R. [A dedicated ambulatory system for the primary health care of the deaf people] Sante Publique. 2014;26:205–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]