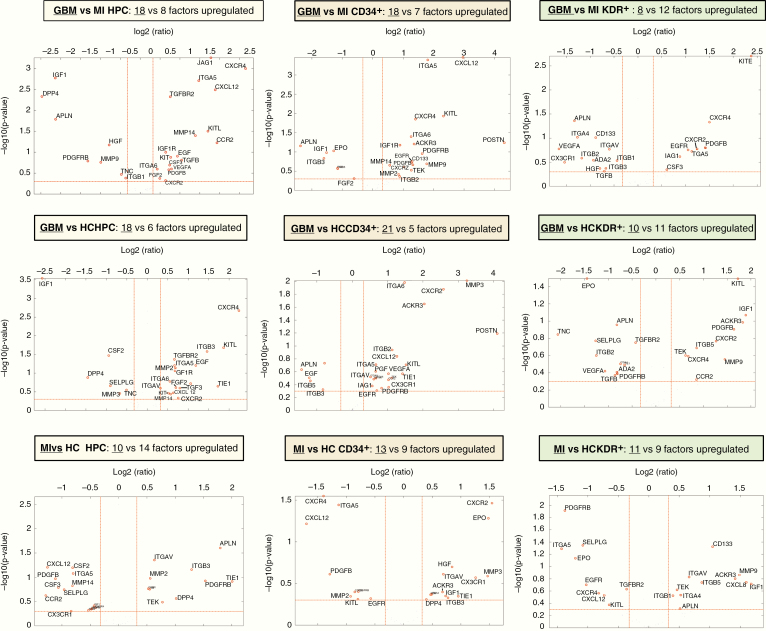
Figure 3.
Volcano plots of gene expression differences between patients and controls by CAC subset. Upper row (A–C): Volcano plots (−log10 P-value vs log2 fold change (FC) with the following cutoff values: FC > l1.25l, P < .5) of GBM versus MI CACs. More genes are overexpressed in GBM versus MI CACs. Overexpressed genes belong to all functional groups. Specifically, there is higher expression in GBM versus MI CACs (especially, HPCs and CD34+ cells) of growth factor receptors (GFRs), chemotactic receptors (CRs), and mobilization factors (MFs). There is higher expression in GBM versus MI HPCs of proangiogenic factors (PAFs). Z-scores and P-values of gene expression in GBM versus MI CACs are given in Figure 5. Middle row (D–F): Volcano plots (−log10 P-value vs log2 FC with the following cutoff values: FC > l1.25l, P < .5) of GBM versus HC CACs. A similar overall pattern of higher gene expression is seen as in the comparison of GBM versus MI CACs. Overexpressed genes belong to all functional groups. Higher expression in GBM versus HC CACs (especially, HPCs and CD34+ cells) of GFRs, CRs, MFs, adhesion factors (ITGs), PAFs. Lower row (G–I): Volcano plots (−log10 P-value vs log2 FC with the following cutoff values: FC > l1.25l, P < .5) of MI versus HC CACs. Overall gene expression is similar/lower in MI CACs versus HC CACs. Lower expression is seen in MI versus HC HPCs for PAFs, CRs, and MFs.