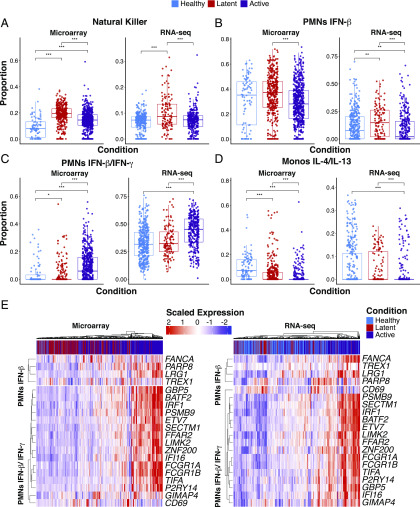
FIGURE 5.
Statistical deconvolution of bulk expression profiles indicates role of IFN-induced neutrophil response in M. tuberculosis infection. (A–D) Proportion estimates for neutrophils, Monocytes and NK cells from CIBERSORT with our MCCS signature matrix (B–D) and immunoStates (A) for eight microarray datasets and five RNA-Seq datasets (Supplemental Table II). (E) Scaled expression of 20 genes found in our neutrophil–IFN signatures are shown for the RNA-Seq and microarray samples as well as the disease status of the sample. Sample sizes for each disease state and data type are as follows; healthy (microarray n = 88, RNA-Seq n = 365), latently infected (microarray n = 376, RNA-Seq n = 117), and active disease individuals (microarray n = 547, RNA-Seq n = 306). Significance was determined by Kruskal–Wallis rank sum test with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.