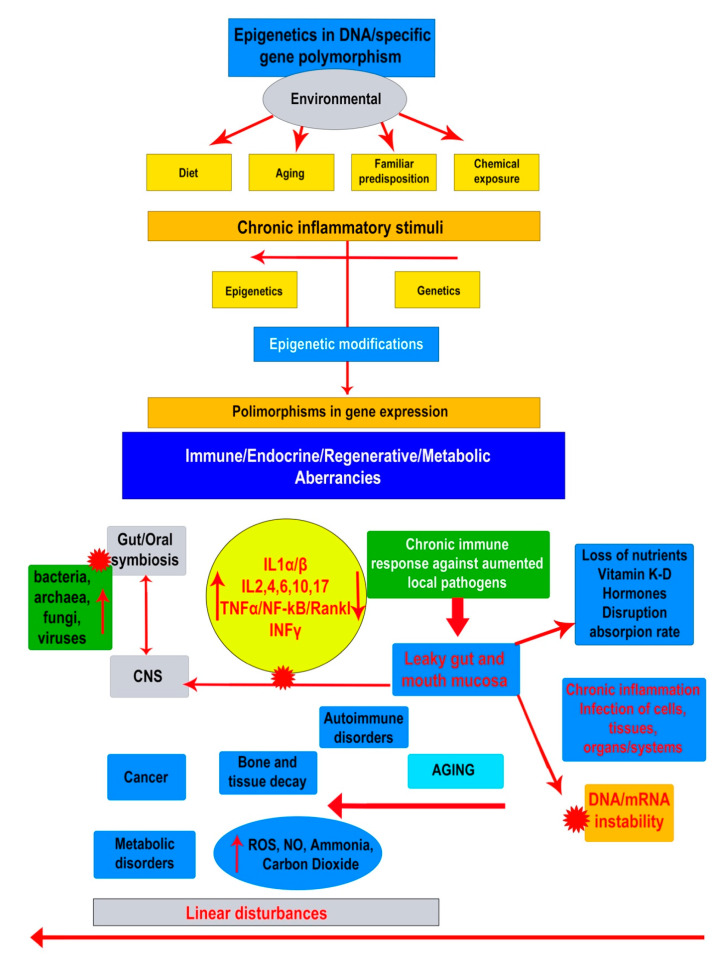
Figure 1.
The proposed schematic representation of how the dysbiosis may eventually interfere the whole organism functionality. Environmental risk factors such as life style and food may negatively influence the microbiome raising up the activity of bacteria, fungi and viruses that lead the immune system towards a state of progressive pro-inflammatory activity through the presence of TNF-a, IFNy, Interleukins. Bidirectional signaling between the oral-gastrointestinal tract and central nervous system (CNS) occurs through spinal afferents demonstrate that these two systems showed some similarities in terms of expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and altered physiological functions and have increased awareness about the epigenome and microbiome, highlighting a plausible link between the gut microbiome and epigenetic modification of the host. This has explained the intensification of various diseases such as immune-mediated, metabolic, and cardiovascular diseases and cancer. Two arrow head indicates e bidirectional communication between two systems.  Indicates the high negative impact of agent or group of agents on a different system or another compound, as bacteria, viruses and fungi on oral/gut eubiosis.
Indicates the high negative impact of agent or group of agents on a different system or another compound, as bacteria, viruses and fungi on oral/gut eubiosis.