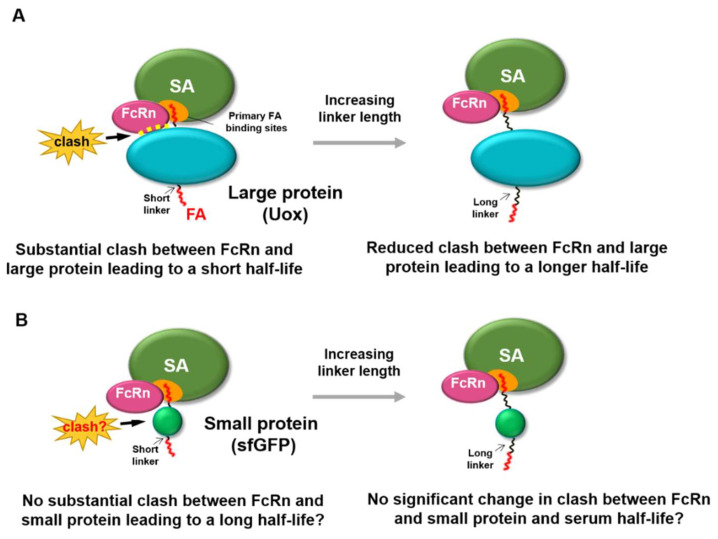
Figure 1.
Effect of protein size of fatty acid-conjugated protein on the binding of FcRn with serum albumin. (A) For a large protein (Uox, 140 kDa), conjugation of fatty acid with a short linker leads to steric hindrance to binding of FcRn to serum albumin, due to its large size. Increasing the linker length reduces the steric hindrance to binding of FcRn to serum albumin, resulting in longer serum half-life. (B) For a small protein (superfolder green fluorescent protein [sfGFP], 28 kDa), conjugation of a fatty acid with a short linker may not exhibit substantial steric hindrance to binding of FcRn to serum albumin, due to its small size. Therefore, increasing linker length may not substantially alter the steric hindrance to the binding of FcRn to serum albumin.