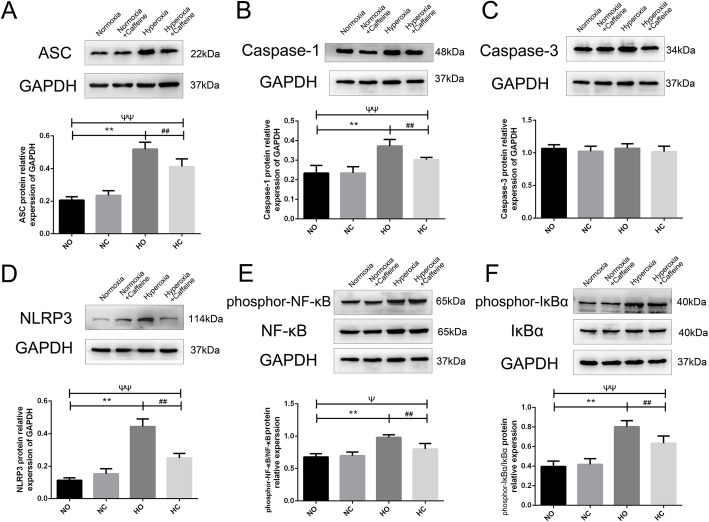
Fig. 6.
The effect of caffeine on the NF-κB pathway and inflammasome proteins in neonatal mouse lung. Hyperoxia exposure led to the activation of the NF-κB pathway and inflammasome proteins. Caffeine treatment ameliorated this hyperoxia-induced change. a Representative image and semiquantitative analysis of ASC protein expression in lung tissue. b Representative image and semiquantitative analysis of Caspase-1 protein expression in lung tissue. c Representative image and semiquantitative analysis of Caspase-3 protein expression in lung tissue. d Representative image and semiquantitative analysis of NLRP3 protein expression in lung tissue. e Representative image and semiquantitative analysis of phosphor-NF-κB and NF-κB protein expression in lung tissue. f Representative image and semiquantitative analysis of phosphor-IκBα and IκBα protein expression in lung tissue. GAPDH was the loading control. The values are the mean ± SD; n = 6 mice/group. **P < 0.01 Hyperoxia (HO) group versus Normoxia (NO) group, ##P < 0.01 Hyperoxia + Caffeine (HC) group versus HO group, ΨP < 0.05, ΨΨP < 0.01 NO group versus HC group