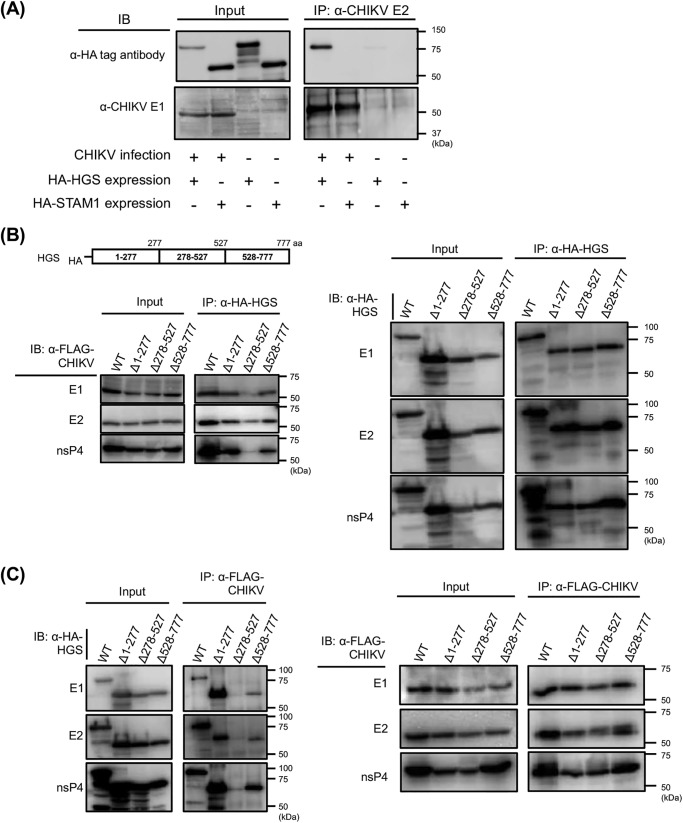
Figure 3.
Interactions between CHIKV and HGS analyzed by co-IP. A, either HA-tagged HGS or HA-tagged STAM1 was exogenously introduced into HEK293T cells, following CHIKV infection. Interactions between CHIKV and either HGS or STAM1 were analyzed by co-IP. Anti-CHIKV E2 mAb (5.5G9) was utilized for IP, and either anti-HA tag or anti-CHIKV-E1 antibody (CK47) was used to detect each ESCRT proteins or CHIKV E1 protein. B, genome organization of HGS is shown in the schematic at the top. HGS truncated mutants were lacking either amino acid residues 1–277, 278–527, or 528–777 from WT HA-tagged HGS, designated as Δ1–277, Δ278–527, or Δ528–777, respectively. Interactions between CHIKV and truncated HGS mutants were analyzed by co-IP. HA-tagged truncated HGS mutants or full-length HGS, and FLAG-tagged CHIKV proteins were exogenously introduced into HEK293T cells. Following anti-HA IP, individual FLAG-tagged CHIKV proteins (left) or individual HA-tagged host factors (right) in each fraction were detected by immunoblotting (IB) using the cell lysates. C, reciprocally with Fig. 3B, anti-FLAG mAb was utilized for IP, and anti-HA mAb was utilized for detection of HA-tagged HGS mutants.