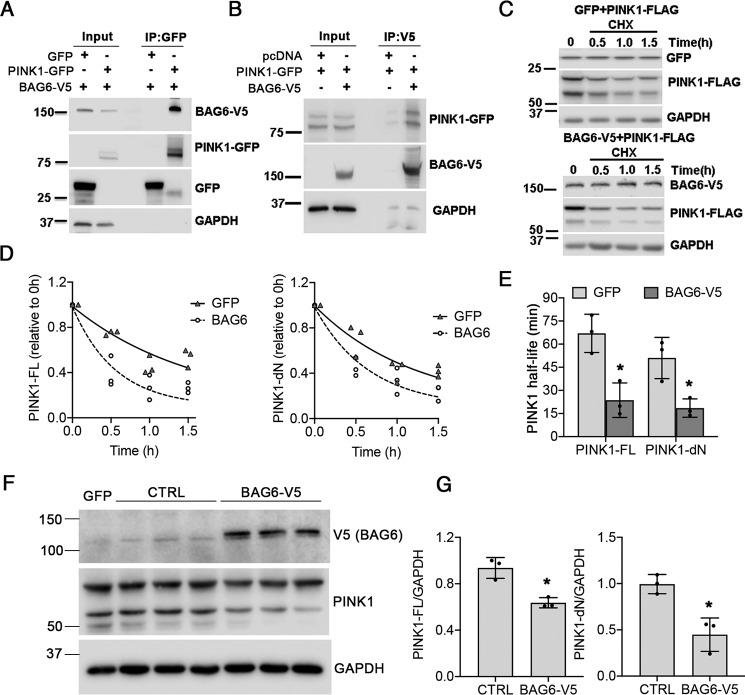
Figure 6.
BAG6–PINK1 interaction and PINK1 turnover. A, co-immunoprecipitation of BAG6-V5 in PINK-GFP pulldowns from transfected HEK293 cells. B, co-immunoprecipitation of PINK1 by V5-tagged BAG6 in transfected HEK293 cells. C and D, overexpression of BAG6-V5 accelerated the loss of co-transfected FLAG-tagged PINK1 in cycloheximide-treated HEK293 cells compared with cells co-overexpressing GFP and FLAG-tagged PINK1. E, the half-life of PINK1 isoforms was estimated by fitting a one-phase exponential decay curve for each independent experiment using Prism 8 software (GraphPad). For PINK1-FL, *, p = 0.0084 for BAG6-V5 versus GFP. For PINK1-dN, *, p = 0.0430 for BAG6-V5 versus GFP. F and G, steady-state levels of endogenous PINK1 was determined by transfecting SH-SY5Y cells with 2 μg/well of V5-tagged BAG6 plasmid or vector control. GFP transfection was used to monitor transfection efficiency and normalize densitometry ratios. For PINK1-FL, *, p = 0.0066 for BAG6-V5 versus Ctrl. For PINK1-dN, *, p = 0.0104 for BAG6-V5 versus Ctrl. All graphs represent means ± S.D., n = 3 independent experiments, two-tailed Student's t test.