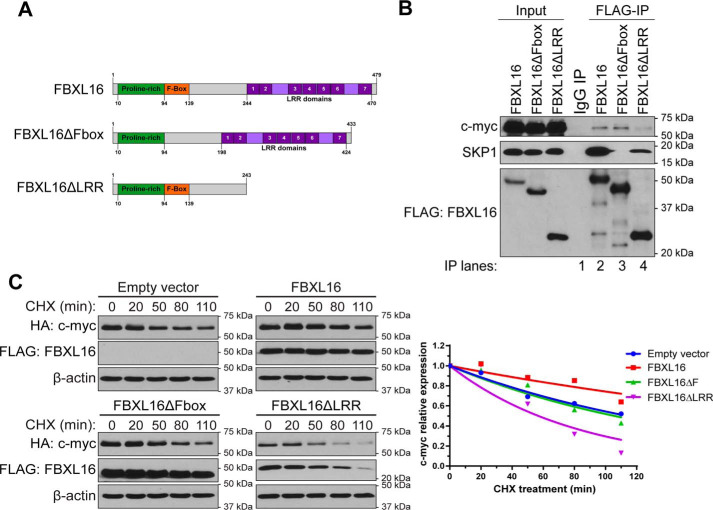
Figure 5.
Both F-box and LRR domains of FBXL16 are important for the regulation of c-myc. A, schematic structures of full-length FBXL16 protein, FBXL16 with the deletion of F-box domain (FBXL16ΔFbox), and FBXL16 with the deletion of the c-terminal LRRs (FBXL16ΔLRR). The numbers below or above the structures indicate the positions of the amino acids. B, FLAG-tagged FBXL16, FBXL16ΔFbox, or FBXL16ΔLRR was overexpressed in 293T cells, followed by immunoprecipitation using anti–FLAG-Ab conjugated agarose beads (FLAG-IP). Western blot analysis was then performed to examine the interactions of FBXL16 or the deletion mutant with endogenous SKP1 and c-myc proteins. C, HeLa cells were transiently co-transfected with HA–c-myc together with either an empty vector control, FLAG-FBXL16, FLAG-FBXL16ΔFbox, or FLAG-FBXL16ΔLRR. 32 h post transfection, protein translation was inhibited with CHX (100 μg/ml) for different times (minutes), followed by cell lysis and Western blot analysis of protein levels. c-myc protein level at each time point was normalized to that of β-actin, and the normalized c-myc protein level at 0 min time point was arbitrarily set as 1. Exponential curves were extrapolated using the one-phase exponential decay model (GraphPad Prism 6 software).